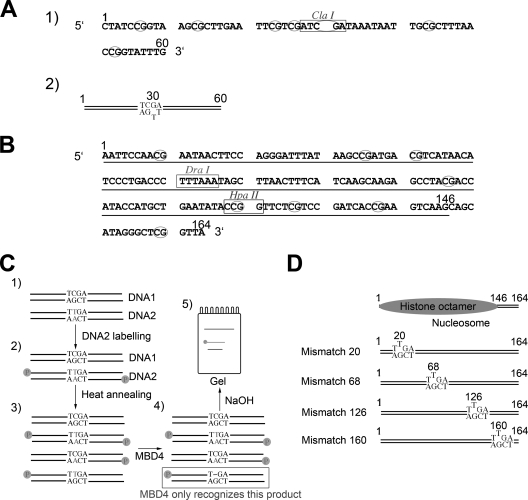
FIG. 1.
Preparation of T/G mismatch DNA templates used for the analysis of MBD4 glycosylase activity. (A) Sequence of a 60-bp synthetic DNA duplex used for this analysis. CpG dinucleotides are circled. The ClaI site used to assess the methylation of CpGs is shown. (B) Nucleotide sequence of the 164-bp fragment of the 5S rRNA gene of the sea urchin L. variegatus used for the nucleosome reconstitution work. The 1 and 164 positions are identified, and the main position occupied by the histone octamer in nucleosomes reconstituted from this DNA template is underlined. (C) Steps: 1, two versions (DNA1 and DNA2) of the 164-bp fragment depicted in panel B were constructed with the sequence altered in one to introduce a mismatch; 2, unlabeled (DNA1) and labeled (DNA2) DNA constructs were mixed in stoichiometric amounts; 3, DNA fragments in the mixture were melted and reannealed and were used in nucleosome reconstitution and glycosylase assays; 4 and 5, the glycosylase activity of MBD4 was assessed by NaOH cleavage of the resulting unpaired nucleotide. (D) Schematic representation of the constructs generated by the introduction of mismatches into the 164-bp sequence of the 5S rRNA gene fragment. The position occupied by the histone octamer in these constructs is also shown (Fig. 6).