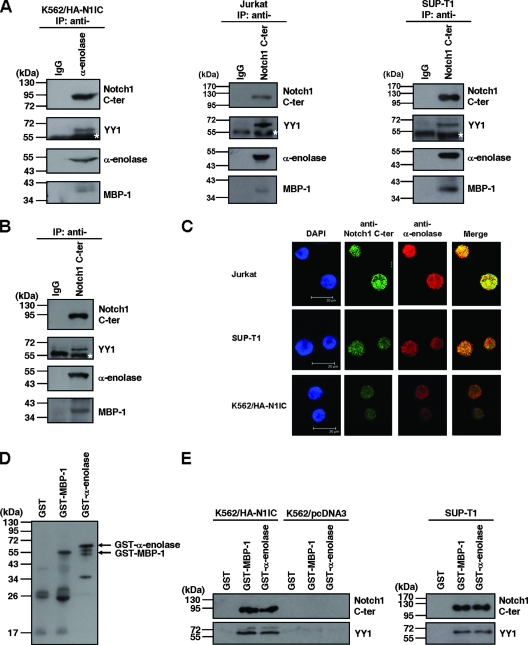
FIG. 1.
N1IC associates with α-enolase and MBP-1. (A) Whole-cell extracts of N1IC-expressing K562/HA-N1IC cells (left), Jurkat cells (middle), and SUP-T1 cells (right) were prepared for coimmunoprecipitation using anti-IgG, anti-α-enolase, and anti-Notch1 C-ter antibodies. The precipitated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot analysis using anti-Notch1 C-ter antibody. The immunoblot was stripped and then reprobed with anti-YY1 and anti-α-enolase antibodies, sequentially. Note the anti-α-enolase antibody can recognize both α-enolase and MBP-1 (18). (B) Nuclear extracts of K562/HA-N1IC cells were prepared for coimmunoprecipitation using anti-IgG and anti-Notch1 C-ter antibodies. The precipitated proteins were analyzed by Western blot analysis using anti-Notch1 C-ter, anti-YY1, and anti-α-enolase antibodies. (C) The localizations of the Notch1 receptor intracellular domain and α-enolase or MBP-1 were assessed by immunofluorescence staining and confocal microscopy. Slides were incubated with goat anti-Notch1 C-ter or rabbit anti-α-enolase antibodies and subsequently with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated donkey anti-goat IgG or Alexa Fluor 568-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG. Cell nuclei were also stained by DAPI. (D) Purified GST, GST-MBP-1, and GST-α-enolase fusion proteins were analyzed by Western blot analysis using anti-α-enolase antibodies. (E) Whole-cell extracts of K562/HA-N1IC, K562/pcDNA3, and SUP-T1 cells were used for pull-down assay with purified GST, GST-MBP-1, and GST-α-enolase fusion proteins. The pull-down pellets were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Notch1 C-ter (upper panel) or anti-YY1 (lower panel) antibodies. The immunoblots shown here are representative of three or four independent experiments. IP, immunoprecipitated proteins. The white stars indicate the heavy chain of antibody used for immunoprecipitation.