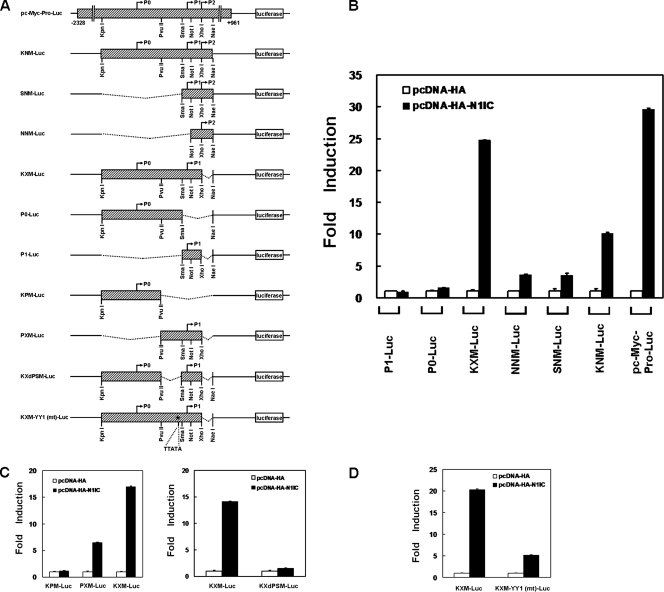
FIG. 2.
The YY1 response element is important for transactivation of c-myc by N1IC. (A) Schematic representation of luciferase reporter plasmids containing various lengths of the human c-myc promoter. The reporter plasmid pc-Myc-Pro-Luc contains the full-length c-myc promoter. The P0, P1, and P2 promoters transcribing the c-myc gene and restriction enzymes cleavage sites are shown. The hatched boxes represent the sequence of the c-myc promoter. The star indicates the position of the putative YY1 response element which was mutated in the KXM-YY1 (mt)-Luc reporter plasmid. (B) Reporter plasmids containing various lengths of the c-myc promoter were cotransfected with the N1IC expression construct (pcDNA-HA-N1IC) or its control vector (pcDNA-HA) into K562 cells. (C) Reporter plasmids (left, KPM-Luc, PXM-Luc, and KXM-Luc; right, KXdPSM-Luc and KXM-Luc) containing various lengths of the c-myc promoter were cotransfected with the pcDNA-HA-N1IC expression construct or pcDNA-HA control vector into K562 cells. (D) Both KXM-Luc and KXM-YY1 (mt)-Luc reporter plasmids containing wild-type or mutated YY1 response elements in the c-myc promoter were cotransfected with the pcDNA-HA-N1IC expression construct or pcDNA-HA control vector into K562 cells. Two days after transfection, luciferase activity was determined from whole-cell extracts, and the basal promoter activity of reporter construct was set to unity. Values are means and standard deviations from at least three independent experiments.