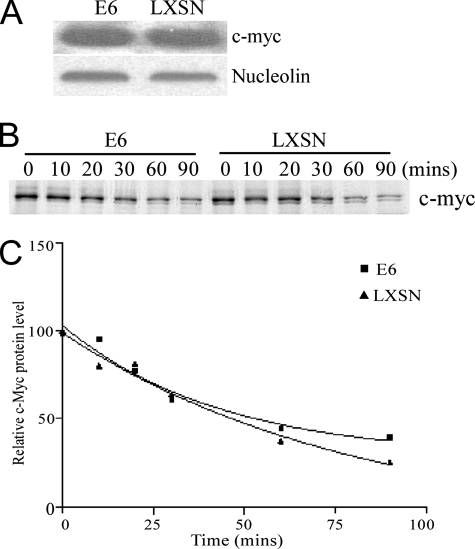
FIG. 1.
c-Myc steady state and half-life in E6- and LXSN-expressing HFKs. (A) Western blot of whole-cell lysates from HPV16 E6-HFK and LXSN-HFK cells. c-Myc was detected with mouse anti-c-Myc antibody (with nucleolin as a loading control). (B) c-Myc pulse-chase analysis in LXSN-HFKs and HPV16 E6-HFKs. Cells were pulse-labeled with [35S]methionine for 10 min and chased for the indicated times. c-Myc was immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti-c-Myc antibody and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. (C) The signal in panel B was visualized and quantitated by a PhosphorImager analysis. Nonlinear regression was performed with Prism software. The r2 values of the E6 and LXSN samples are 0.9689 and 0.9738, respectively. A paired t test was performed (P = 0.18).