Figure 4.
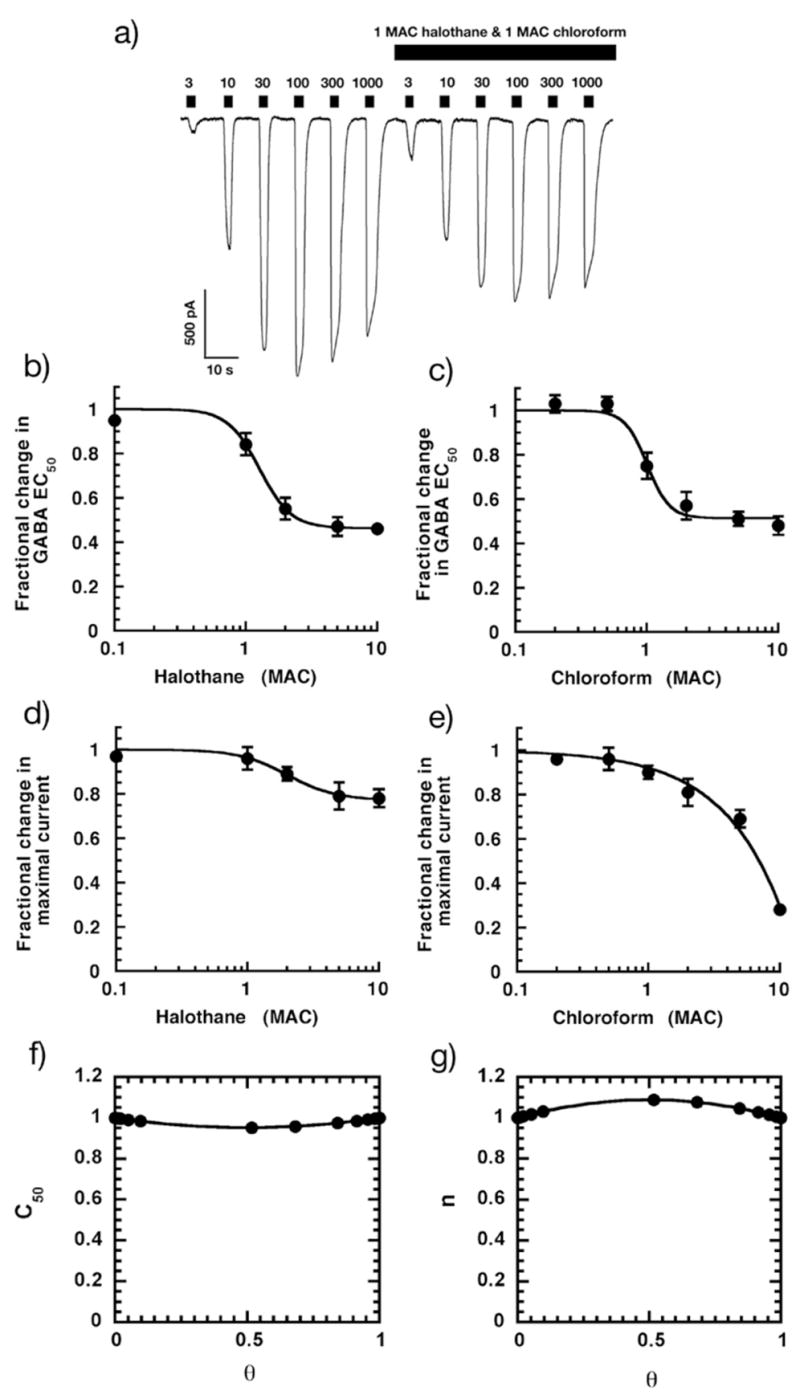
Responses in HEK-293 cells voltage clamped at −60mV expressing α1β2γ2s GABAA receptor subunits to 0.3 – 1000 μM GABA are modulated by 220 μM halothane and 900 μM chloroform (1 MAC of each). a) Halothane and chloroform enhance the amplitude of currents when applied together at lower (<10 μM) but depressed at greater concentrations of GABA. Calibration bars indicate the amplitude and duration of the responses. b) Halothane enhances GABAA receptor function by reducing the GABA EC50. c) Cloroform enhances GABAA receptor function by reducing GABA EC50. d) Halothane reduces maximal GABAA receptor function. e) Chloroform reduces maximal GABAA receptor function. f) & g) Halothane and chloroform are additive in their ability to decrease GABA EC50. C50 and n were determined using the methods described and plotted in the range 0 < θ ≤ 1. Both C50 and n did not significantly deviate from unity indicating that there is no significant synergism or antagonism between the two anesthetics in the reduction of GABAAR EC50.
