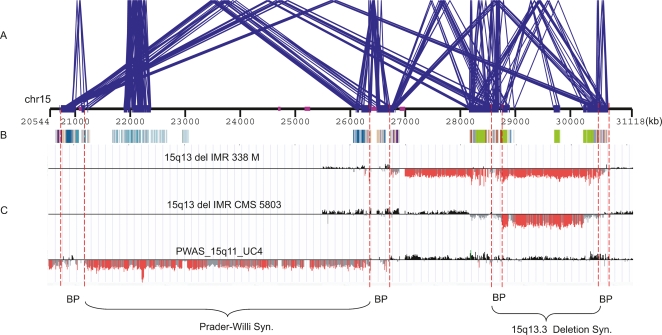
Figure 3.
Duplication architecture flanking genomic disorders. This figure shows the duplication architecture defined by DupMasker for one of the most unstable regions of the human genome (15q11–15q13). (A) Blue lines delineate intrachromosomal duplications of high-sequence identity (size ≥10 kb and sequence identity ≥95%) within this region (WGAC) and identify four breakpoint regions associated with Prader-Willi/Angelman Syndrome and the 15q13.3 deletion syndrome. (B) The duplication substructures defined by DupMasker are depicted as color-coded boxes with different colors representing different cytogenetic band locations of duplicons. (C) ArrayCGH data from one patient with Prader-Willi syndrome (bottom) and two patients with chr15q13.3 deletion (Sharp et al. 2008) indicate the patients’ deletion breakpoints overlap with the duplicons defined by DupMasker. The locations of the breakpoint intervals are highlighted by red dashed lines.