Figure 1.
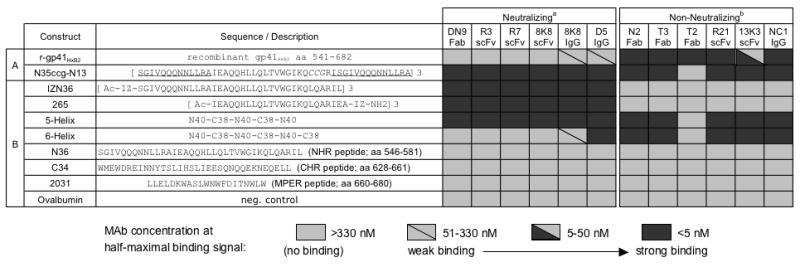
Binding by ELISA of mAbs against a panel of immobilized gp41 mimetic antigens. MAbs were titered in parallel against (A) r-gp41HxB2 and N35CCG-N13, used in the initial mAb screening process, and (B) a panel of gp41 mimetics and peptides. The mAb concentrations at half-maximal binding were determined and are represented using shaded boxes: strong binding (<5 nM, dark), moderate binding (5-50 nM, half dark), weak binding (51-330 nM, light with diagonal line), and no detectable binding (>330 nM, light). MAbs designated as a, ‘Neutralizing’, and b, ‘Non-neutralizing’ were found to neutralize HIV-1HxB2 with an IC50<100 nM, and an IC50>~4 μM in a single-round infectivity assay, respectively (see text).
