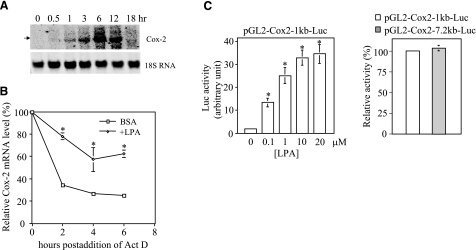
Figure 3.
Effect of LPA on Cox-2 expression involves both transcriptional activation and post-transcriptional enhancement of Cox-2 mRNA stability. A) Analysis of the steady-state levels of Cox-2 mRNA. Caov-3 cells were stimulated with 10 μM LPA for the indicated periods of time. Total cellular RNA was extracted and analyzed by Northern blotting. The membrane was reprobed for 18S RNA to show equal loading among samples. B) Measurement of Cox-2 mRNA stability. Caov-3 cells were treated for 6 h with LPA (10 μM) or BSA (control) before addition of actinomycin D (Act D, 5 μg/ml). Total RNA was isolated from the cells at 0, 2, 4, and 6 h after addition of Act D. The relative Cox-2 mRNA levels were determined by RT-qPCR and plotted as a function of hours postaddition of Act D. The values at 0 h were defined as 100%, with other time points presented as relative percentages. C) Reporter analysis of the Cox-2 gene promoter. Caov-3 cells transfected with pGL2-Cox2–1kb-Luc containing the –980 to +15 fragment of the Cox-2 promoter were stimulated with LPA at the indicated concentrations for 6 h and assayed for luciferase activity (left panel). LPA-induced luciferase activity from Caov-3 cells transfected with pGL2-Cox2–1kb-Luc (defined as 100%) was compared with the activity from the cells transfected with pGL2-Cox2–7.2bk-Luc (right panel). All numeric results are means ± sd of triplicates, representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05.