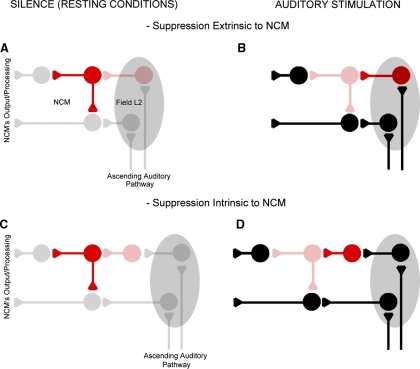
FIG. 8.
Anatomical-functional NCM model. This simplified model suggests that under resting conditions, spontaneously active GABAergic synapses suppress NCM's excitatory network and that on auditory stimulation, spontaneously active GABAergic synapses are suppressed by a secondary inhibitory network that is inactive at rest and that is activated by auditory stimuli. The inhibition of spontaneously active GABAergic synapses could arise from locations remote to NCM, such as field L (A and B), as well as from GABAergic neurons intrinsic to NCM (C and D). GABAergic neurons are illustrated in red while excitatory cells are black; bright colors indicate activated neurons while faded colors illustrate resting cells.