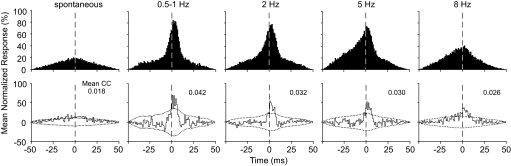
FIG. 11.
Effect of stimulus frequency on septa–MI coordination. Top and bottom rows depict the raw and shifted-corrected CCGs, respectively, for 6 neuronal pairs that displayed significant correlations during each frequency. Each CCG was constructed by normalizing each neuron pair to the maximum frequency response of pair, dividing by the number of stimuli, and then summing across neuron pairs to produce a population CCG. Each CCG lists the mean correlation coefficient. Dotted lines indicate 99% confidence intervals; bin widths: 1 ms.