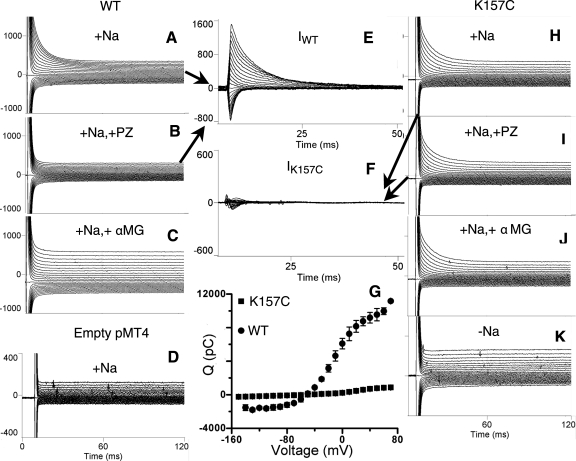
Fig. 2.
Representative pre-steady-state transient currents generated with a voltage clamp over a range of −150 mV to +70 mV in oocytes expressing wild-type (WT) and mutant K157C, in the presence and absence of 0.2 mM phloridzin (PZ) or 10 mM α-methyl-d-glucopyranoside (αMG). In all cases, the Na+ concentration was 100 mM, except for K, in which currents were measured at 0 mM Na+. A: WT transient currents. B: WT transient currents after exposure to PZ. C: WT transient currents after exposure to αMG. D: transient currents from an oocyte injected with empty pMT4 plasmid. E: WT-specific PZ-sensitive transient currents (IWT). F: K157C-specific PZ-sensitive transient currents (IK157C). G: charge transfer (Q) characteristics of WT rSGLT1 (n = 3) compared with K157C rSGLT1 (n = 5). H: K157C transient currents. I: K157C transient currents after exposure to PZ. J: K157C transient currents after exposure to αMG. K: K157C transient currents in 0 mM Na+.