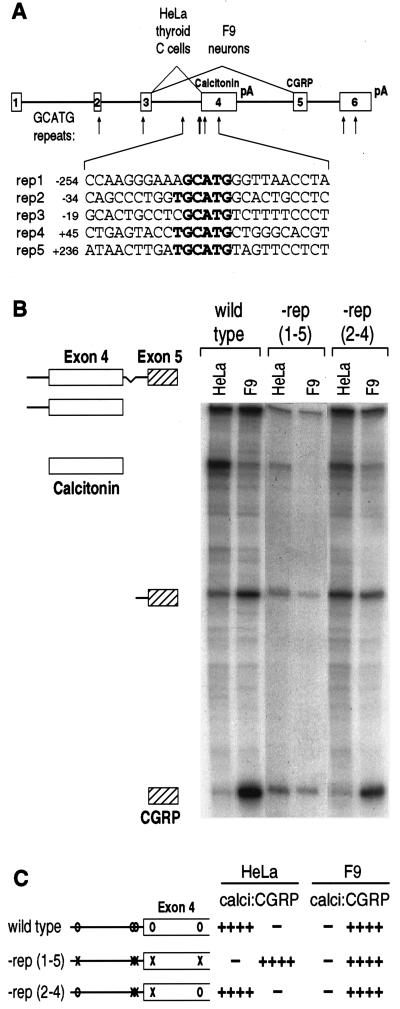
Figure 1.
GCATG repeats are necessary for calcitonin-specific splicing. (A) The structure of the rat calcitonin/CGRP gene is diagrammed, indicating the location of GCATG repeats (arrows). The sequence of each repeat and flanking sequences is given below. (B) Total RNAs from stably transfected HeLa and F9 cells were analyzed by RNase protection. Cells were transfected with the wild-type gene, or with mutant genes lacking all five of the repeats indicated in A, −rep (1–5), or the central three repeats, −rep (2–4). Protected fragments are identified at the left. (C) Quantitative results from RNase protections is shown graphically. For ease of identification, mutations in individual repeats are shown by an “X,” whereas the wild-type repeat is indicated by “O.” Note that the quantitative data are corrected for the difference in the specific activities of the calcitonin- and CGRP-specific protected fragments.