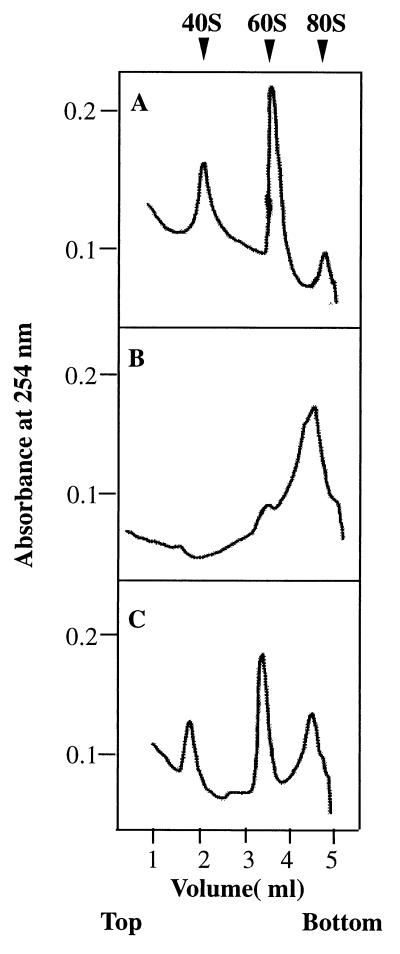
Figure 5.
Ribosomal subunit anti-association activity of bacterially expressed recombinant eIF6. eIF6 activity was measured by its ability to bind to a 60S ribosomal subunit and prevent its association with the 40S ribosomal subunit to form an 80S ribosome as described (14, 15). Reaction mixtures (100 μl each) contained 20 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 7.5/100 mM KCl/1 mM MgCl2/1 mM DTT/0.4 A260 unit (8 pmol) of 80S ribosomes. In addition, in the reaction in C, 300 ng (12 pmol) of purified recombinant eIF6 was added whereas the other two reactions in A and B did not contain eIF6. After incubation at 30°C for 5 min, the Mg2+ concentration of reaction mixtures in B and C was raised to 5 mM whereas the Mg2+ concentration of the reaction in A was kept at 1 mM, and the incubation continued for another 5 min at 37°C. Under these conditions, ribosomal subunits generated by dissociation of 80S ribosomes at 1 mM Mg2+ during the first incubation should reassociate during the second incubation at 5 mM Mg2+ to 80S ribosomes provided no eIF6 was present in the incubation mixture. In contrast, when eIF6 was present during the first incubation, 60S⋅eIF6 particles formed would fail to associate with 40S particles to form 80S ribosomes during the second incubation. Reaction mixtures were then chilled in an ice–water bath, layered onto 5-ml linear 5–30% (wt/vol) sucrose gradients containing 20 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 7.5, 100 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT, 5 mM MgCl2 (for reactions in B and C) and 1 mM MgCl2 (for reaction in A only), and centrifuged in a SW 50.1 rotor for 90 min at 48,000 rpm. The gradients were analyzed in an ISCO model 640 gradient fractionator, and the absorbance profile at 254 nm was analyzed by using the UA-5 absorbance monitor.