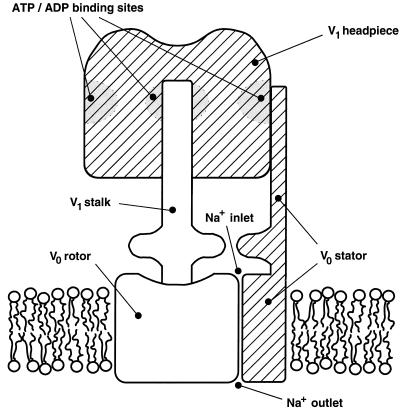
Figure 4.
Model of the molecular V-ATPase motor. ATP hydrolysis in the V1 headpiece drives rotation of the central stalk. The stalk transmits the rotation to the V0 rotor. Rotation of the rotor against the stator structure results in the pumping of Na+ ions across the membrane at the interface. Hatched parts are static, and open parts are rotating.