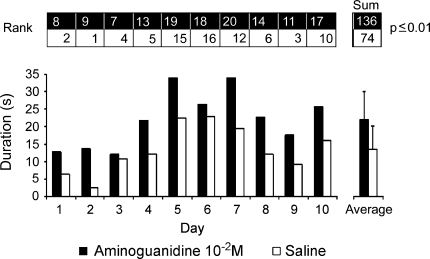
Fig. 2.
Male song-stimulated sound production in aminoguanidine (AG)- and saline-injected female grasshoppers. Two groups of eight C. biguttulus females were stimulated with calling songs of conspecific males at 4–5 h after receiving an injection of 30 μl AG (10−2 M) or saline on ten consecutive days. Each column in the main graph represents the sum of the responses of all eight females on the respective experimental day. Male song-stimulated sound production was higher in AG treated females (black columns) than in saline-injected controls (white columns) on each experimental day. This difference is also reflected in the average daily response over the entire experimental period (right). Comparison of all female responses over the entire experimental period with a non parametric rank-based test (ranks indicated above main graph) revealed a highly significant difference (P ≤ 0.01; U-test after Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney) in the average duration of sound production between AG- and saline-treated grasshopper females