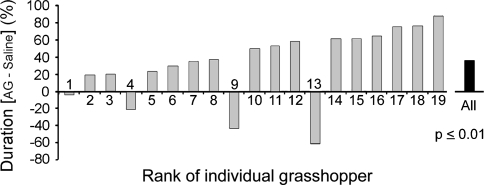
Fig. 3.
Male song-stimulated sound production in aminoguanidine (AG)- and saline-injected female grasshoppers. Two groups of C. biguttulus females were injected alternately with 30 μl AG (10−2 M) and saline, and stimulated with male calling songs, on four consecutive days. One group started with AG treatment on day 1 while the other started with saline treatment. There was no difference in the overall responsiveness to male song between the two groups with different starting treatment. The graph displays the differences of male song-stimulated sound production following AG (sum of 2 days) and saline injection (sum of 2 days) for 19 individual female grasshoppers. Sixteen of the females were more responsive to male song after AG treatment than after saline injections [highly significant difference (P ≤ 0.05) in Wilcoxon’s matched pairs signed rank test]. Comparison of the responses from all experiments with the 19 females over the entire experimental period revealed a significant difference between the duration of sound production following AG treatment and its duration after saline injections (P ≤ 0.025; U-test after Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney; data not shown)