Figure 2. Caspase-3 is increased during differentiation and is essential for proper differentiation of ES cells.
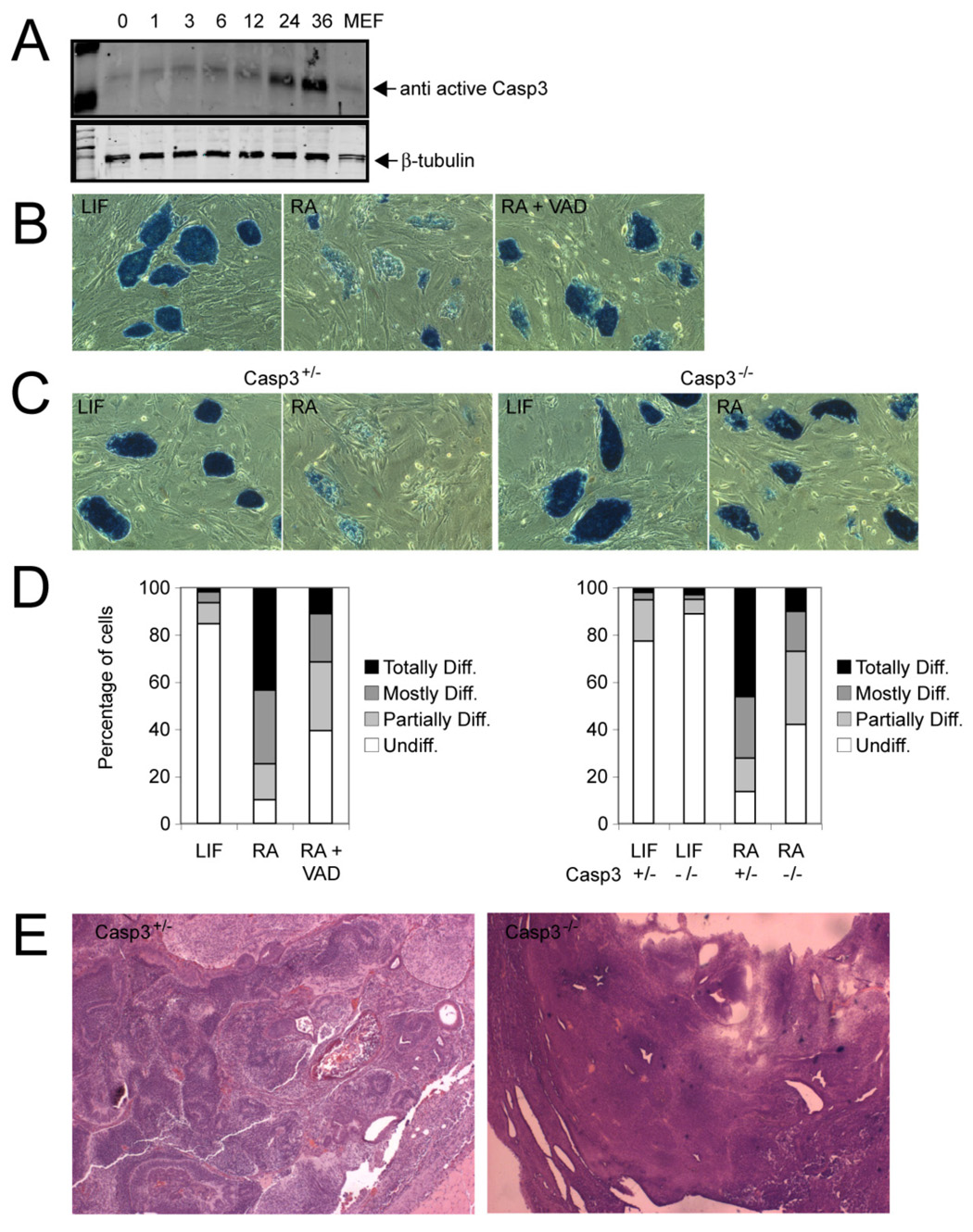
(A) Western blot analysis of protein lysates from ES cells stimulated to differentiate with RA for the indicated times. The Western blot membranes were probed with an antibody that specifically recognizes only active Caspase-3. MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblasts. (B) Alkaline phosphatase staining of ES cell colonies stimulated with RA (1 µM/ml) or coincubated with RA and the pan-Caspase blocking peptide VAD.fmk (100 µM) after 3 days. Cells incubated with leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) served as controls. The majority of colonies lost staining due to differentiation, whereas coincubation with VAD prevented differentiation. Magnification, 10X. (C) Casp3 heterozygous (+/−) and knockout (−/−) ES cells were stimulated with RA (1 µM) for 3 days and stained for alkaline phosphatase. Casp3+/− ES cells differentiated, whereas the majority of Casp3−/− ES cells did not (10X). Controls were cells incubated without LIF (D, left) Quantification of colonies shown in panel B as described in Experimental Procedures. Mean values are shown. (D, right) Quantification of colonies shown in panel C. Mean values are shown. (E) Casp3+/− and Casp3−/− ES cells were injected into immunocompromised nude mice, and the resultant tumors were analyzed histologically. Typical aspects of Casp3+/− and of Casp3−/− tumors included derivatives from all three germ layers within a teratoma or immature and undifferentiated cells, respectively.
