Figure 1. Summary of SOP development in wild type and Notch mutant backgrounds.
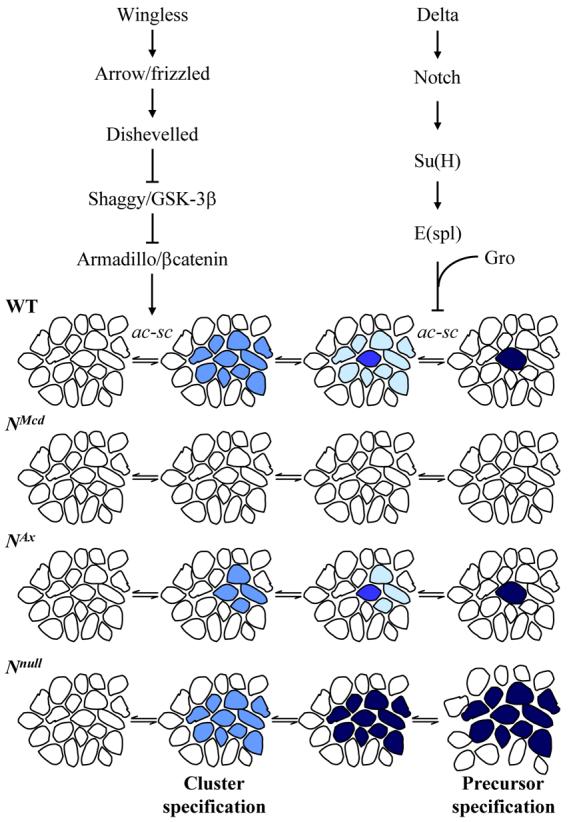
In wild type flies, the combined action of the prepattern genes and signalling through the Wingless pathway leads to the expression of proneural genes of the achaete-scute complex in small groups of cells. All the cells within these proneural clusters have the potential to develop into SOPs. However lateral inhibition signalling restricts achaete-scute expression to one or two cells. These cells will divide three times to produce the socket, bristle, supporting, glial and neural cells of the sensory bristles. In the NMcd and NAx mutants there is increased Notch signalling via Deltex which represses proneural gene expression. This signalling prevents proneural cluster specification in NMcd flies and consequently no SOPs develop. In NAx mutants the increase in signalling via Deltex is not as great and proneural clusters of reduced size develop. The process of lateral inihibition then restricts proneural gene expression to one cell. Both signalling via Deltex and lateral inhibition are abolished in Nnull clones leading to robust achaete-scute expression and the development of multiple SOPs.
