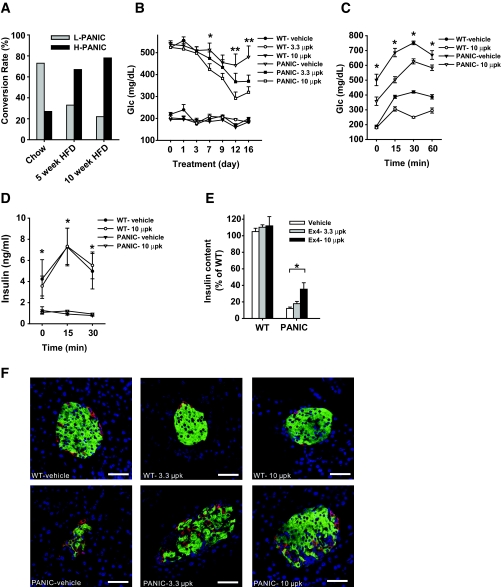
FIG. 3.
Exendin-4 treatment improves the pancreatic β-cell recovery after ablation. A: Conversion rate of hemizygous PANIC-ATTAC mice into low responders (L-PANIC) and high responders (H-PANIC) after high-fat diet (HFD) treatment of 0, 5, and 10 weeks. n = 6–22 per group. B: Glucose profile of wild-type and PANIC-ATTAC mice with vehicle and exendin-4 treatments. Wild-type and hemizygous PANIC-ATTAC mice were on high-fat diet for 4 weeks, and hyperglycemia was induced by dimerizer injection. Postprandial blood glucose levels were recorded. Significant differences are found between PANIC-vehicle and PANIC-10 μpk groups at days 7, 12, and 16. In each wild-type group, five animals were used, and seven animals were used per PANIC-ATTAC group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001. C: OGTT of wild type and PANIC-ATTAC with vehicle and exendin-4 treatments. Significant differences are seen between vehicle and exendin-4 treatments over the entire course for PANIC-ATTAC. Wild-type vehicle, n = 5; wild-type 10 μpk, n = 5; PANIC-vehicle, n = 7; PANIC-10 μpk, n = 7. Note that exendin-4 treatment in wild-type animals also shows significant differences at 30 and 60 min compared with vehicle. *P < 0.05. D: Insulin levels during OGTT for wild-type and PANIC-ATTAC mice of vehicle and exendin-4 groups. The same animals of C were analyzed. Note that significant difference is seen between wild-type and PANIC-ATTAC mice independent of exendin-4 treatment. *P < 0.05. E: Pancreatic insulin content of wild type and PANIC-ATTAC after vehicle and exendin-4 treatments. Significant difference was found between vehicle and exendin-4 treatments (10 μpk) for PANIC-ATTAC. At least three animals were recorded per group. *P < 0.05. F: Immunofluorescent staining for insulin (green), glucagon (red), and nuclei (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. (Please see http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/db07-1631 for a high-quality digital representation of this figure.)