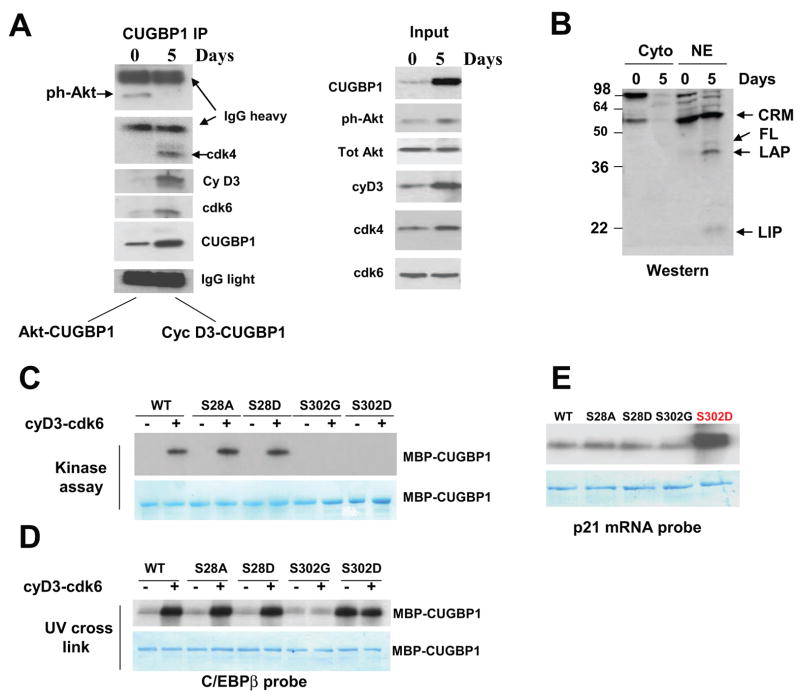
Figure 2. Cyclin D3-cdk4/6 increases binding of CUGBP1 to C/EBPβ and p21 mRNAs in differentiated myotubes.
A. CUGBP1 is associated with “active” Akt in proliferating myoblasts, while in differentiated myotubes CUGBP1 is associated with cyclinD3/cdk4/6. Left image. Co-IP-Western blotting. CUGBP1 was immunoprecipitated from proliferating and differentiated C2C12 cultured cells. “0” and “5” show days of culturing cells in fusion medium. These IPs were probed with antibodies to ph-Akt, cyclin D3, CUGBP1, cdk4 and cdk6. Light and heavy chains of IgGs are shown and revealed that equal amounts of CUGBP1 antibodies which were used for CUGBP1 precipitation from myoblasts and from myotubes. Right image (input) shows Western blotting of the cytoplasmic extracts used for the CUGBP1 IPs. B. The levels of CUGBP1 translational target, C/EBPβ, are increased in normal differentiated muscle cells. The cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies to C/EBPβ. The full-length and truncated C/EBPβ proteins (LAP and LIP) are shown by arrows. CRM; cross-reactive molecule. C. Cyclin D3-cdk6 phosphorylates CUGBP1 at S302. WT CUGBP1 and CUGBP1 mutants (shown on the top) were incubated with cyclinD3/cdk6 complex and 32P-γATP in in vitro kinase assay. The membrane was stained with coomassie to show loading of CUGBP1 proteins (bottom image). D. Phosphorylation of CUGBP1 by cyclinD3/cdk6 increases its binding to C/EBPβ mRNA. UV cross link was performed with un-phosphorylated CUGBP1 and CUGBP1 phosphorylated by cyclin D3/cdk6 using the C/EBPβ mRNA probe. Coomassie blue shows equal amounts of CUGBP1 used in this experiment. E. A phosphomimetic CUGBP1-S302D strongly interacts with the 5′ region of p21 mRNA. UV cross link was performed with non-phosphorylated wild type and mutant CUGBP1 proteins. Coomassie staining on the bottom shows equal amounts of purified CUGBP1-MBP used in these experiments.