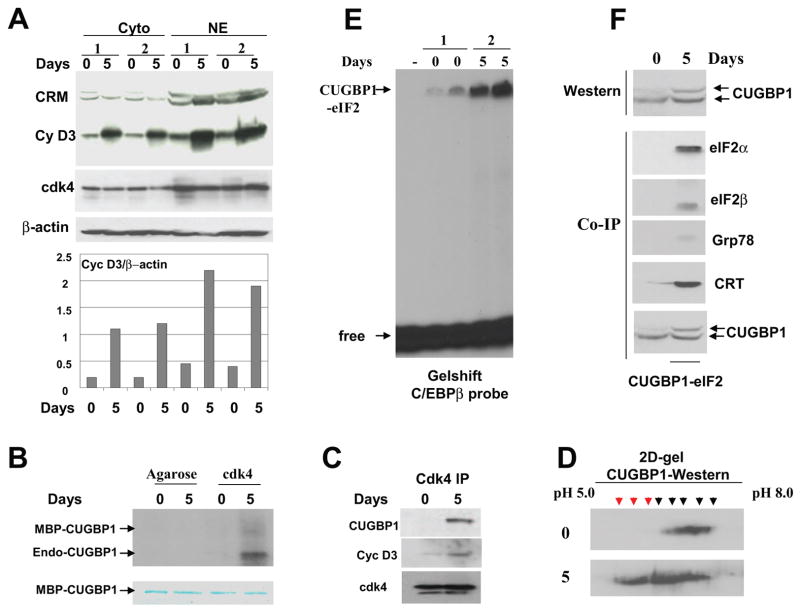
Figure 3. The phosphorylation of CUGBP1 by cyclin D3/cdk4 during differentiation of C2C12 cells correlates with increased amounts of the CUGBP1-eIF2 complex.
A. Cyclin D3 levels are increased in cytoplasm and in nuclei of C2C12 myotubes. Western blotting of cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts isolated from two sets of C2C12 cells subjected to differentiation (days 0 and 5) was performed with antibodies against cyclin D3 and cdk4. The membrane was re-probed with Abs to β-actin as control. Cross reactive molecule (CRM) is shown and serves as an internal control for the loading. Bar graphs show protein levels of cyclin D3 as ratios to β-actin. B. Cdk4 phosphorylates CUGBP1 in normal myotubes. Cdk4 was precipitated from myoblasts (0) and myotubes (5) and examined in kinase assay with MBP-CUGBP1 as a substrate. Arrows show the positions of MBP-CUGBP1 and endogenous CUGBP1 interacting with cdk4 in myotubes. Phosphorylation of the endogenous CUGBP1 is more efficient relatively to the MBP-CUGBP1 purified from bacteria. Bottom part is a commassie stain of the membrane which shows the equal amounts of MBP-CUGBP1 used in this assay. C. CUGBP1 and cyclin D3 are abundant in cdk4 IPs from C2C12 myotubes. Western blotting was performed with cdk4 IPs using antibodies to CUGBP1 and cyclin D3. D. Phosphorylation of CUGBP1 is increased in differentiated myotubes. 2D-gel-electrophoresis-Western blotting of protein extracts from C2C12 myoblasts (top) and myotubes (bottom) with antibodies to CUGBP1. The 2D-We stern was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Phosphorylated CUGBP1 isoforms with similar mobility in myoblasts and in myotubes are shown by black arrows. Additional hyper-phosphorylated isoforms of CUGBP1 in myotubes are shown by red arrows. E. The amounts of the high molecular weight complex migrating in the position of CUGBP1-eIF2 are increased in differentiated myotubes. EMSA assay was performed with two sets of cytoplasmic extracts from mouse C2C12 myoblasts and myotubes using C/EBPβ RNA as a probe. The high molecular weight complex binding with C/EBPβ probe (putative CUGBP1-eIF2) is shown by arrow. F. The translational CUGBP1-eIF2 complex is increased in differentiated myotubes. Top. Amounts of CUGBP1 and phosphorylation of CUGBP1 are increased during normal differentiation. Western blotting was performed with extracts isolated from myoblasts (0) and from myotubes (5). Bottom. The amounts of CUGBP1-eIF2 complex are increased in differentiated C2C12 cells. CUGBP1 was immunoprecipitated from cytoplasms of myoblasts (0) and from cytoplasm of myotubes (5 days), and these IPs were probed with antibodies to the components of the CUGBP1-eIF2 complex (shown on the right).