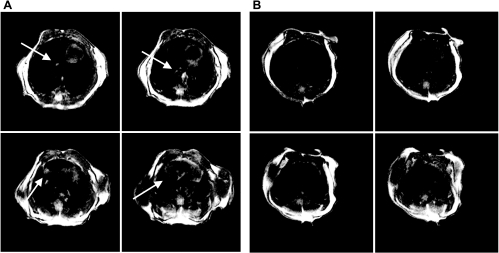
Fig. 1.
Representative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI; 4 axial sections, 1 mm thick) of a mouse thorax that 6 h earlier received intratracheal (IT) interleukin (IL)-1β + tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (arrows indicate inflamed areas) (A) or received IT placebo (sterile saline) (B). Diffuse infiltrates are apparent in the images of the IL-1β+TNF-α-treated mouse. These changes corresponded to a hyperintense-to-total lung volume (HTLV) ratio of 0.15 compared with the placebo-treated mouse, for which the ratio was 0.04.