FIGURE 4.
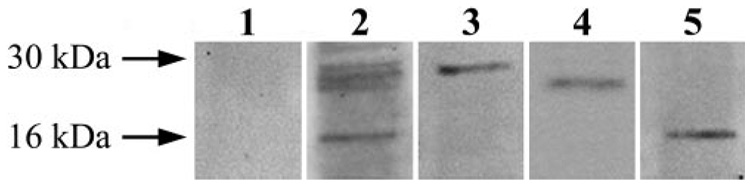
Isolation of 14-3-3– containing protein complexes. To detect proteins interacting with 14-3-3, 14-3-3– containing protein complexes were eluted through coimmunoprecipitation using antibodies against different 14-3-3 isoforms. As a complementary approach to elute 14-3-3– containing protein complexes, recombinant protein-based affinity pull-down was also performed using GST-tagged 14-3-3 protein isoforms. Eluted 14-3-3– containing protein complexes were then subjected to gel-free mass spectrometric analysis to identify proteins interacting with 14-3-3. SDS-PAGE was performed to confirm the purified protein complexes before their mass spectrometric analysis. Lanes 1 and 2 indicate protein staining of gels obtained using a control immunoprecipitate with IgG or the immunoprecipitate with 14-3-3 antibody, respectively. Lanes 3, 4, and 5 are immunoblots of the 14-3-3 immunoprecipitate shown in lane 2 using 14-3-3, Bad, or calmodulin antibodies, respectively. Because no band was detected in the negative control, these data verify that the proteins subsequently identified through mass spectrometric analysis are molecular constituents of the 14-3-3 protein complex. Western blot analysis using specific antibodies also confirm the results of mass spectrometric protein identification that the proteins interacting with 14-3-3 include Bad and calmodulin.
