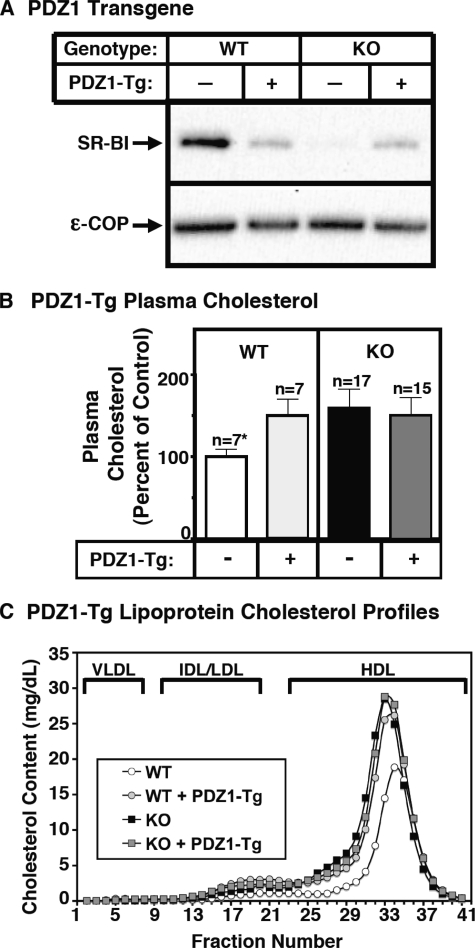
FIGURE 4.
Effect of expression of the PDZ1 transgene on hepatic SR-BI protein levels (A) and plasma lipoprotein cholesterol (B and C) in WT and PDZK1 KO mice. A, liver lysates (∼30 μg of protein) from mice with the indicated genotypes, with (+) or without (-) the PDZ1 transgene, were analyzed by immunoblotting, and SR-BI (∼82-kDa band) was visualized by chemiluminescence. ε-COP (∼34 kDa) was used as a loading control. Note the faint SR-BI band in the nontransgenic PDZK1 KO lane. B and C, plasma was harvested from mice with the indicated genotypes and PDZ1 transgene. B, total plasma cholesterol levels were determined in individual samples by enzymatic assay, and results from the indicated numbers of animals (n) were pooled by genotype and normalized to the mean value for WT plasma cholesterol (100% = 131.7 mg/dl). Independent WT and KO control animals for each founder line were generated to ensure that the mixed genetic backgrounds for experimental and control mice are matched. *, the nontransgenic WT plasma cholesterol levels were statistically significantly different (p ≤ 0.001) from those plasma cholesterol levels of WT[PDZ1-Tg], PDZK1 KO, and PDZK1 KO[PDZ1-Tg] mice. C, plasma samples (harvested as in B) from individual animals were size-fractionated by FPLC, and the total cholesterol content of each fraction was determined by an enzymatic assay. The chromatograms are representative of multiple individually determined profiles. Approximate elution positions of native very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate density lipoprotein/low density lipoprotein (IDL/LDL), and HDL particles are indicated by brackets and were determined as previously described (19).