Figure 7.
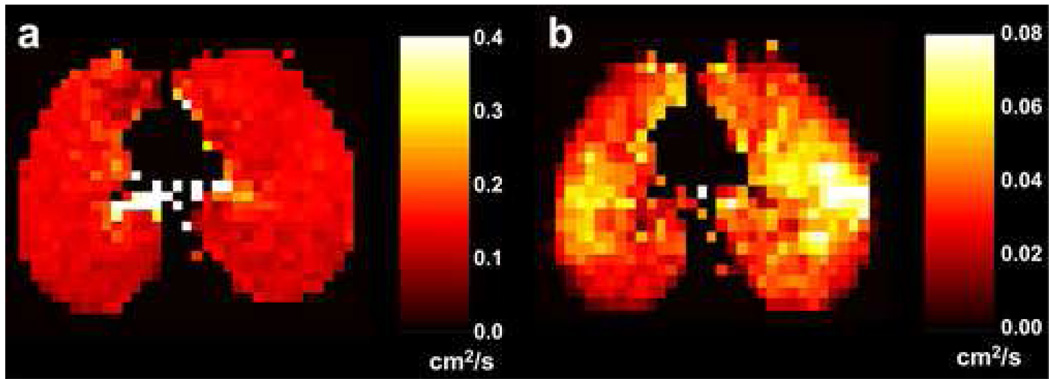
Axial short-time-scale (a) and long-time-scale (b) ADC maps from a subject with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The diffusion times were 2 ms and 1.0 s for the short-time-scale and long-time-scale measurements, respectively. The ADC values are quite uniform within the lung parenchyma in the short-time-scale ADC map (the elevated values are gas within large airways), while local elevations of the ADC are seen in both lungs in the long-time-scale ADC map. Parameters for the short-time-scale, gradient-echo acquisition included: TR, 11.0 ms; TE, 6.7 ms; flip angle, 3°; b values, 0 and 1.6 s/cm2; diffusion-sensitization direction, head-foot. Parameters for the long-time-scale, stimulated-echo acquisition included: TR, 6.4 ms; TE for stimulated echoes, 7.0 ms; TE for calibration data, 1.3 ms; flip angle, 5°; tag wavelength, 10 mm; diffusion-sensitization direction, head-foot. Parameters common to both acquisitions included: in-plane resolution, 5.9 × 5.9 mm2; slice thickness, 40 mm.
