Figure 3. Nbs1 is important for Mre11 localization and the inhibition of E4 mutant DNA replication.
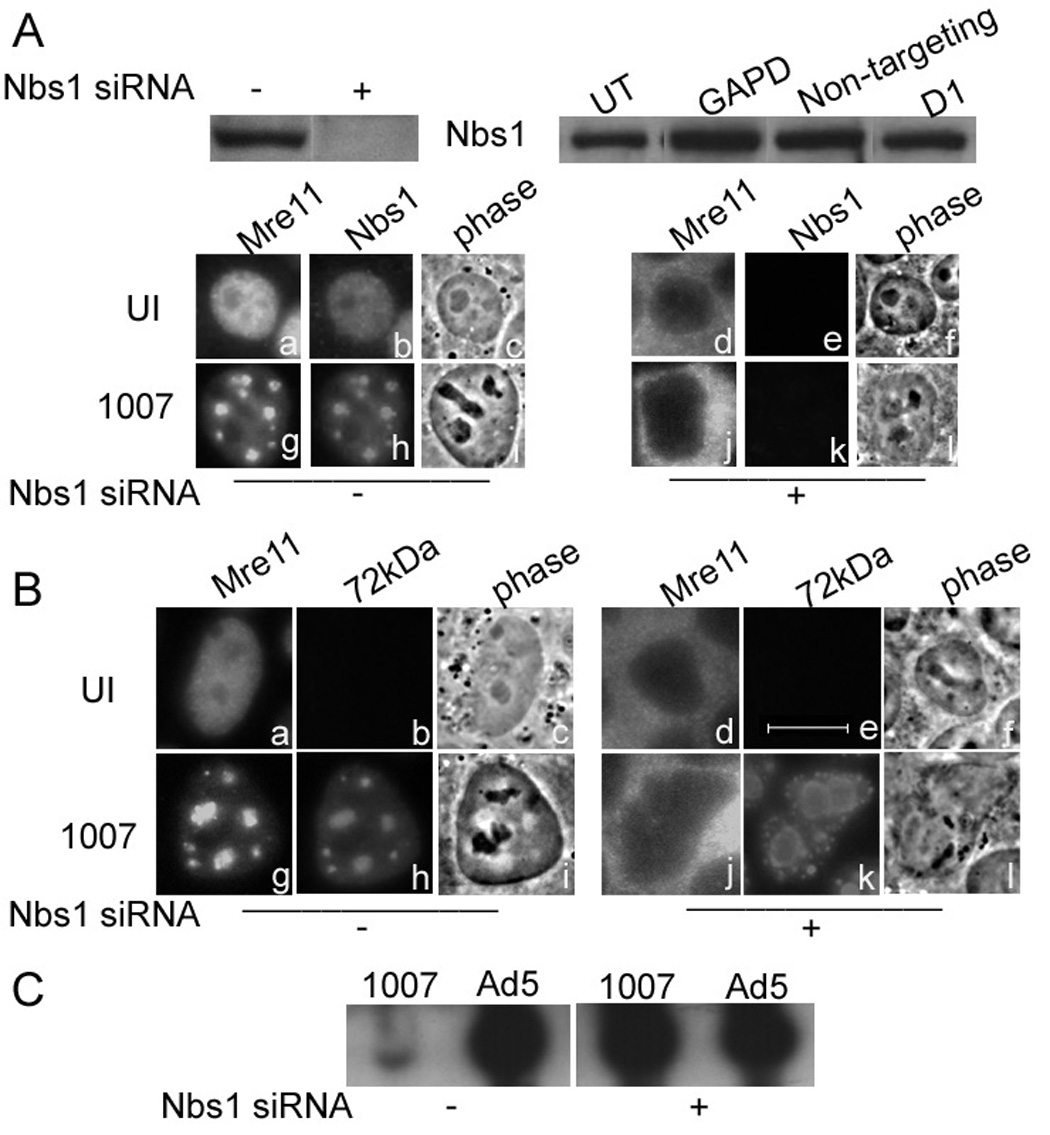
HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA or Nbs1 siRNA prior to infection with Ad5 or H5dl1007 at 3 FFU/cell for 24h. (A) Nbs1 knockdown was monitored by western blotting using 75µg of total protein prepared 96 hours after mock (−) or Nbs1 specific siRNA (+) transfection, using goat polyclonal Ab against Mre11. Additional controls demonstrating the specificity of Nbs1 expression knockdown included no treatment (UT), non-targeting siRNA (non targeting), siRNA against GAPD, and treatment with the transfection reagent alone (D1). Mre11 and Nbs1 distribution in untransfected, uninfected cells (panels a to c) and cells infected with H5dl1007 (Panels g to i) for 24 h are shown. The distribution of Mre11 and Nbs1 in siRNA transfected HeLa cells that were either uninfected or infected for 24 h with H5dl1007 are shown in panels d to f and j to l respectively. (B) Mre11 and viral E2-72kDa protein distribution in untransfected cells that were either uninfected (panels a–c) or infected (panels g to I) are shown. The distribution of Mre11 and E2-72kDa distribution in Nbs1 siRNA transfected cells that were either uninfected or infected with H5dl1007 is shown in panels d to f and j to l, respectively. Bar 10µm. (C) Levels of viral DNA synthesis in Ad5 and H5dl1007 infected HeLa with (+) and without (−) Nbs1 siRNA transfection were quantified by Southern analysis of 10µg of Eco RI digested total DNA prepared at 24 hpi. The C fragment from the DNA digestion was used to compare Ad5 and H5dl1007 DNA levels.
