Figure 3.
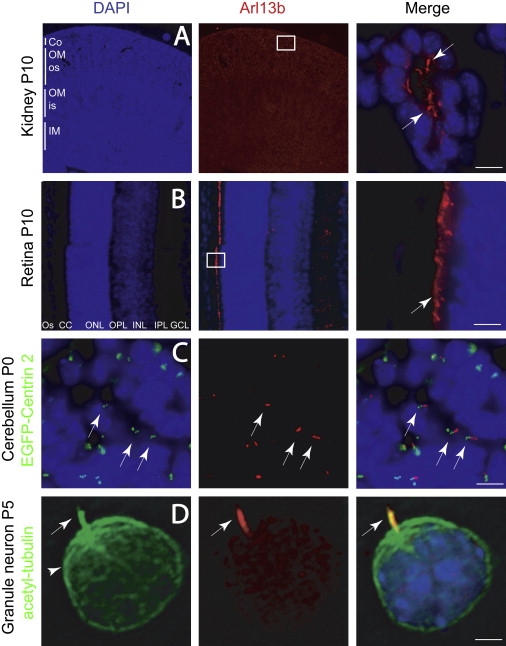
Arl13b Localization in Cilia within Kidney, Retina, and Developing Cerebellar Granule Neurons
Boxed region indicates location of high-power field shown in the third panel in (A) and (B).
(A) Kidney tubule shows Arl13b-positive cilia protruding into the lumen (arrows) in close approximation to the epithelial nuclei (blue, DAPI).
(B) Retina shows intense Arl13b staining in photoreceptor connecting cilia layer (CC, arrow).
(C) External granule layer (EGL) of P0 cerebellum from EGFP-Centrin 2 transgenic mouse stained with Arl13b. EGFP-labeled centrioles (green dots, arrow, left) are evident in many cells, defining the position of the basal body. An Arl13b-positive cilium projects adjacent to the basal body in many of these cells (arrows, right).
(D) Acutely dissociated CGN showing cilia (arrow) stained with acetylated tubulin (green) costains with Arl13b (red). Acetylated tubulin also stains the microtubule cytoskeleton (arrowhead), which is negative for Arl13b.
Abbreviations: Co, cortex; os, outer stripe of medulla; is, inner stripe of medulla; OM, outer medulla; IM, inner medulla; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; CC, connecting cilia; OS, outer segment; P, postnatal day. Scale bar represents 20 μm in (A)–(C) and 5 μm in (D).
