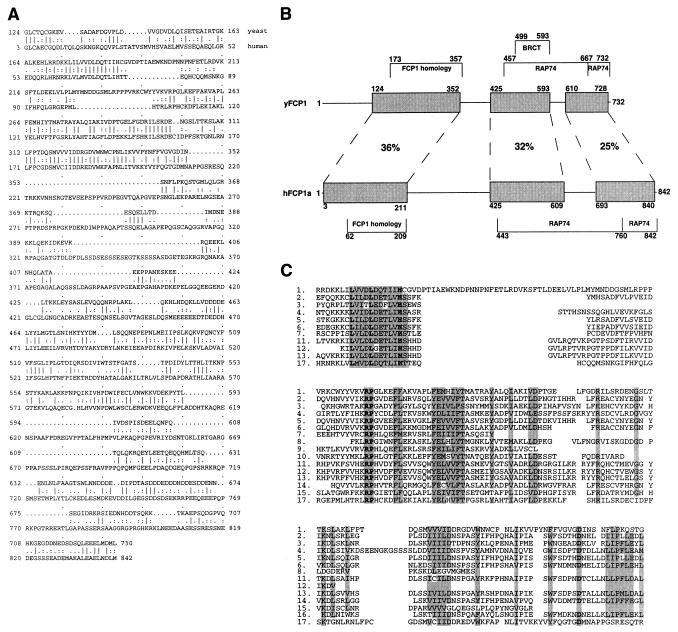
Figure 2.
Sequence and structure of yeast Fcp1. (A) Comparison of yeast and human Fcp1. Amino acid sequences of yeast Fcp1 (top line) and human FCP1a (J.A., H. Xiao, G. Pan, G. Dahmus, M.C., S. Zhang, R. G. Roeder, M. Dahmus, and J.G., unpublished work) (bottom line) were aligned using the sequence alignment program bestfit (Wisconsin sequence analysis package, GCG). Identical amino acids are indicated by a vertical line, highly similar and similar amino acids by a colon and a dot, respectively. (B) Regions of highest similarity and approximate locations of functional motifs in yeast and human Fcp1. Shaded areas are those most similar between yeast and human proteins. “FCP1 homology” refers to the region of similarity presented in C. (C) Multiple alignment of amino acid sequences homologous to yeast Fcp1 residues 173–362 identified by blast searches of GenBank. Bold letters: residues identical in all sequences. Shaded letters: regions of similarity. 1. S. cerevisiae FCP1, Z49704; 2. S. cerevisiae ORF, X90564; 3. S. cerevisiae ORF, U39205; 4. S. cerevisiae ORF, U10555; 5. S. cerevisiae ORF, Z73115; 6. Schizosaccharomyces pombe ORF, Z50142; 7. Brassica campestris EST, L46538; 8. Arabidopsis thaliana EST, T44887; 9. Brugia malayi EST, H48204; 10. Toxoplasma gondii EST, W35521; 11. Caenorhabditis elegans EST, U29536; 12. Mus musculus EST, W29399; 13. Homo sapiens EST, H24417; 14. Homo sapiens EST, H66914; 15. Homo sapiens EST, H95720; 16. Homo sapiens EST, H84869; 17. Homo sapiens FCP1.