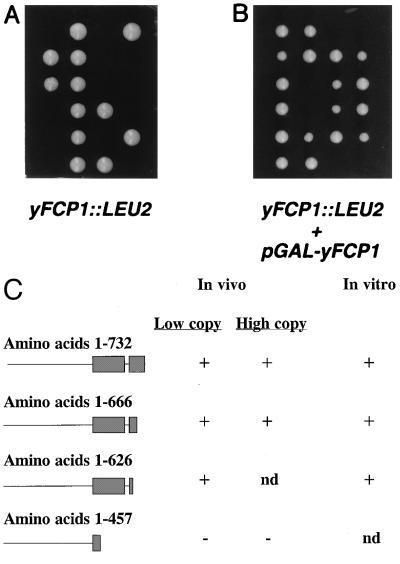
Figure 5.
Yeast FCP1 is essential. (A) Diploid strain JA830 disrupted for one copy of FCP1 was induced to sporulate, and all spores of each tetrad were tested for growth. (B) Diploid JA830 was transformed with pJA754 to produce HA-tagged Fcp1 from the GAL10 promoter. Sporulation was induced, and spores were tested for growth on medium containing galactose. (C) Deletion constructs of Fcp1 were tested for complementation of a strain disrupted for FCP1 in vivo and for phosphatase activity in vitro. Amino acids in each construct and locations of RAP74 interacting regions are indicated. Low copy refers to cells heterozygous for the FCP1 disruption transformed with plasmids containing FCP1 under the control of the endogenous promoter (pJA794, pDB3, pJA796, pDB4, and pJA804); cells were sporulated and growth of haploids was tested on selective media. High copy refers to cells heterozygous for the FCP1 disruption transformed with plasmids containing FCP1 under control of the GAL10 promoter (pJA739, pJA756, and pJA798); cells were sporulated and growth of haploids was tested on medium containing galactose. (+) refers to complementation for viability. The in vitro reactions (19) were carried out with Fcp1 proteins overproduced in E. coli and purified as described in Experimental Procedures; (+) indicates that phosphatase activity was detected. nd, not done.