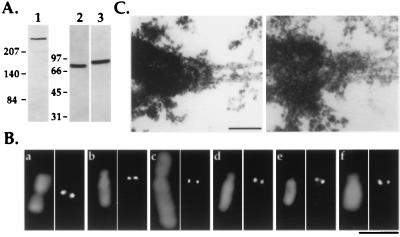
Figure 1.
Reagents for following kinetochore assembly in Xenopus egg extracts. (A) Immunoblots of Xenopus extracts using 1 μg/ml affinity-purified anti-human CENP-E (lane 1), anti-chicken cytoplasmic dynein intermediate chain mAb 70.1 ascites fluid (lane 2), and 0.1 μg/ml affinity-purified anti-XKCM1 (lane 3) antibodies. Extracts were fractionated by 6% SDS/PAGE for CENP-E immunoblots and by 10% SDS/PAGE for dynein and XKCM1 immunoblots. Molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated to the left of each set of panels. (B) Comparative immunofluorescence of CHO (a, c, and e) and A6 (b, d, and f) cell chromosomes using antibodies to CENP-E (a and b), cytoplasmic dynein intermediate chain (c and d), and XKCM1 (e and f). Antibody localizations are shown in the right panel of each pair and DNA in the left panel. (Bar = 5 μm.) (C) Analysis of mitotic XL177 cells by electron microscopy demonstrating the presence of a trilaminar plate kinetochore structure at the point of interaction of kinetochore microtubules with the chromosome. Two separate examples are shown. (Bar = 0.2 μm.)