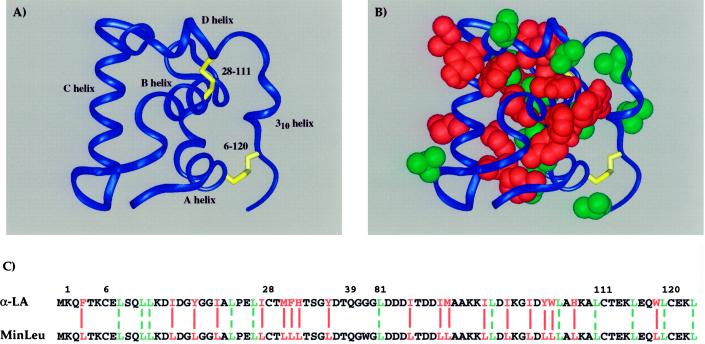
Figure 1.
Hydrophobic sequence minimization of the helical domain of α-lactalbumin. (A) Schematic representation of the helical domain of α-LA based on the structure of full-length human α-LA (55), with helices and disulfide bonds indicated. (B) Hydrophobic side chains in the helical domain of α-LA are highlighted by a space-filling representation. The domain is oriented as in A, with wild-type leucines shown in green and all other hydrophobic side chains, mutated to leucine in the current study, shown in red. (C) Amino acid sequences of the wild-type and minimized helical domains. Residues are numbered in the context of full-length α-LA and colored as in B. Solid red lines align those hydrophobic amino acids in α-LA that are changed to leucine in MinLeu, and dashed green lines align wild-type leucines.