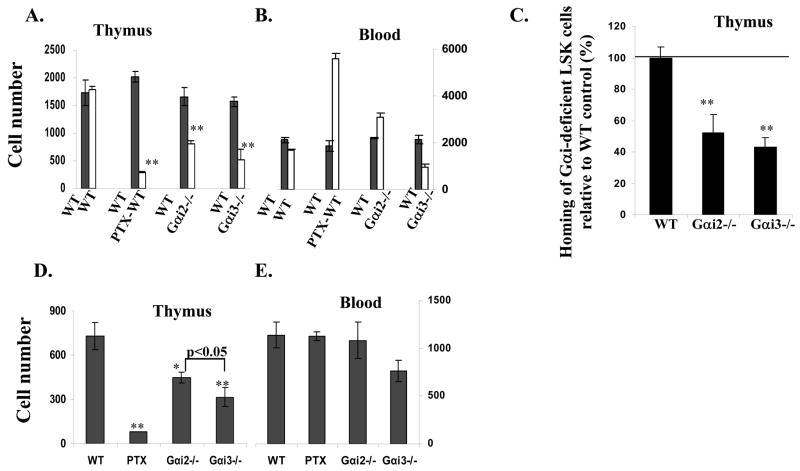
Fig. 5.
Thymic homing depends on Gαi proteins. Wild type (WT) bone marrow cells were labeled with TRITC and mixed with an equal number of CFSE-labeled bone marrow cells of indicated phenotypes (A, B, D, and E). Or, LSK progenitors were sorted from bone marrows of WT, Gαi2−/− and Gαi3−/− mice, fluorescently labeled, and mixed as above (C). The mixtures were injected intravenously into 4.5-week-old WT mice. Thymi (A, C and D) and blood (B and E) were analyzed two days (A, B, and C) or seven days (D and E) later. The data are the means ± SD of the absolute numbers of labeled cells per thymus (A and D) or in a million nucleated blood cells (B and E) of 5 mice in each group. Homing of Gαi2- or Gαi3-deficient LSK cells relatively to WT LSK cells (100%) in the same mouse was shown (C). *, p< 0.05 and ** p<0.01 in the presence vs. absence of Gαi2 or Gαi3.