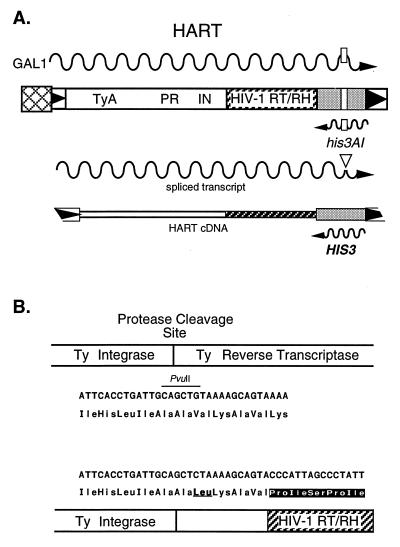
Figure 1.
Hybrid Ty1/HIV-1 RT/RH elements. (A) The RT/RH domain of HIV-1 was used to replace Ty1 RT/RH, resulting in HART (his3AI AIDS Reverse Transcriptase) elements. The inducible galactose promoter-driven hybrid HIV/Ty element marked with his3AI, HART, is shown. his3AI serves as an indicator of passage through an RNA intermediate and of reverse transcription. Expression results in full-length element RNA (wavy line) carrying an antisense copy of his3AI at the 3′ end of the transcript. An artificial intron (open rectangele) interrupts the his3 coding region and is flanked by splice donor and splice acceptor sites such that RNA splicing (▿) of the intron can occur only on the antisense transcript (the sense his3AI transcript is interrupted by a “backward” intron). Splicing, followed by reverse transcription, yields a cDNA copy of the hybrid element carrying a functional HIS3 gene. Integrase (IN)-mediated insertion or cDNA (homologous) recombination of this Ty-HIS3 cDNA results in histidine prototrophy that is scored by genetic selection. Hybrid elements carrying wild-type HIV-1 RT (HART) and the NNRTI-resistant variants HART-L100I and HART-Y181C, along with Ty, can all be assayed for RT activity with this genetic selection. (B) The nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the Ty/HIV-1 RT junction and the Ty protease (PR) cleavage site are shown.