Abstract
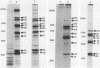
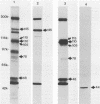
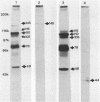
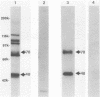
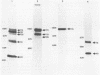
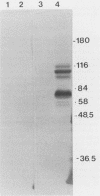
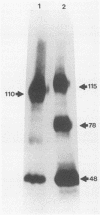
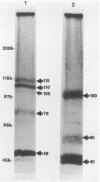
Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 is a gammaherpesvirus which causes malignant catarrhal fever, an acute lymphoproliferative disorder of cattle and other susceptible Bovidae, which is almost invariably fatal. A preliminary analysis of proteins induced by the virus indicated that as many as six glycoproteins and one nonglycosylated molecule might be present in the virus envelope. Monoclonal antibodies selected for recognition of virion envelope proteins included two that recognized a complex of infected cell proteins, designated the gp115 complex, and neutralized virus infectivity in the absence of complement. The gp115 complex consisted of five glycoproteins of 115, 110, 105, 78, and 48 kilodaltons (kDa), and all except the 48-kDa species reacted with antibody in Western blots (immunoblots). Pulse-chase experiments analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing and nonreducing conditions suggested that the 110-kDa protein was the precursor molecule which was processed by addition of sugars to 115 kDa. The 115-kDa protein was cleaved to form a disulfide-linked heterodimer of 78 and 48 kDa, which was the mature form of the molecule incorporated into the virion envelope. The glycoprotein contained N-linked sugars, but little or no O-linked sugar was present. The relative abundance of the mature protein and its ability to induce neutralizing antibodies suggest that it will prove useful to studies aimed at elucidating the biology and pathogenesis of alcelaphine herpesvirus 1.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balachandran N., Pittari J., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Detection by monoclonal antibodies of an early membrane protein induced by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):369–375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.369-375.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boever W. J., Kurka B. Malignant catarrhal fever in greater kudus. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1974 Nov 1;165(9):817–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgen A., Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Reid H. W. Preliminary characterization of the alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 genome. J Gen Virol. 1989 May;70(Pt 5):1141–1150. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-5-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt W. J., Auger D. Synthesis and processing of the envelope gp55-116 complex of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.185-191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Edwards D. P., Weigle K. A., Friedrichs W. E., McGuire W. L. Varicella-zoster virus-specific gp140: a highly immunogenic and disulfide-linked structural glycoprotein. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):138–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby R. O., Buxton D., Reid H. W. The pathology of wildebeest-associated malignant catarrhal fever in hamsters, rats and guinea-pigs. J Comp Pathol. 1988 Jan;98(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(88)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby R. O., Reid H. W., Buxton D., Pow I. Transmission of wildebeest-associated and sheep-associated malignant catarrhal fever to hamsters, rats and guinea-pigs. J Comp Pathol. 1988 Jan;98(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(88)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Clustering of genes dispensable for growth in culture in the S component of the HSV-1 genome. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.3033823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushi E. Z., Rurangirwa F. R. Epidemiology of bovine malignant catarrhal fevers, a review. Vet Res Commun. 1981 Dec;5(2):127–142. doi: 10.1007/BF02214977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOWRIGHT W., FERRIS R. D., SCOTT G. R. Blue wildebeest and the aetiological agent of bovine malignant catarrhal fever. Nature. 1960 Dec 31;188:1167–1169. doi: 10.1038/1881167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid H. W., Buxton D., Pow I., Finlayson J., Berrie E. L. A cytotoxic T-lymphocyte line propagated from a rabbit infected with sheep associated malignant catarrhal fever. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Jan;34(1):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus gene encoding glycoprotein gIII is not essential for growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):635–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.635-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossiter P. B. Antibodies to malignant catarrhal fever virus in cattle with non-wildebeest-associated malignant catarrhal fever. J Comp Pathol. 1983 Jan;93(1):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(83)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth G. R., Reed D. E., Daley C. A., Vorhies M. W., Wohlgemuth K., Shave H. Malignant catarrhal fever in bison. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1977 Nov 1;171(9):913–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford S. E., Little P. B. The gross and histopathologic lesions of maignant catarrhal fever in three captive sika deer (Cervus nippon) in southern Ontario. J Wildl Dis. 1977 Jan;13(1):29–32. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-13.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons J. G., Hutt-Fletcher L. M., Fowler E., Feighny R. J. Studies of the Epstein-Barr virus receptor found on Raji cells. I. Extraction of receptor and preparation of anti-receptor antibody. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1303–1308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Rapid identification of nonessential genes of herpes simplex virus type 1 by Tn5 mutagenesis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):576–579. doi: 10.1126/science.3033824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyand D. S., Helmboldt C. F., Nielsen S. W. Malignant catarrhal fever in ehite-tailed deer. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Sep;159(5):605–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Podack E. R. The ninth component of complement and the pore-forming protein (perforin 1) from cytotoxic T cells: structural, immunological, and functional similarities. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):184–190. doi: 10.1126/science.2425429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., van den Hurk J. V., Gilchrist J. E., Misra V., Babiuk L. A. Interactions of monoclonal antibodies and bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1) glycoproteins: characterization of their biochemical and immunological properties. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):466–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]