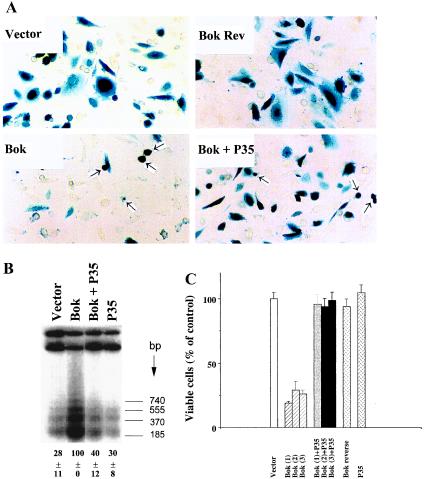
Figure 3.
Overexpression of Bok promotes apoptosis in mammalian cells. (A) Morphology of CHO cells transfected with an expression vector encoding Bok. Normal cell morphology was found in cells transiently transfected with the empty pcDNA3 expression vector (2.1 μg DNA per 35-mm dish) or the vector containing Bok cDNA in reverse orientation (Bok Rev). Cells were also transfected with the Bok expression vector without or with an equal amount of the P35-expressing construct. Arrowheads indicate apoptotic cells whereas darkly stained cells represent transfected cells. (B) Internucleosomal DNA fragmentation induced by Bok and partial inhibition by the baculoviral protease inhibitor P35. CHO cells were treated as described in A. At 18 h after transfection, cellular DNA was extracted for analysis of DNA fragmentation using a 3′end labeling method. Quantitative estimation of low molecular weight DNA is shown at the bottom of the figure (mean ± SEM, n = 3). (C) Quantitative analysis of cell killing by Bok and the inhibitory effects of P35. The number of β-gal-expressing cells (mean ± SEM, n = 3) was determined at 36 h after transfection. Data from cells transfected with three independent clones (1, 2, and 3) encoding Bok are presented as a percentage of viable cells in the control group. CHO cells were transfected with a total of 2.1 μg plasmid DNA including 2.0 μg of pcDNA3 expression constructs and 0.1 μg of the pCMV-β-gal reporter. In cells transfected with two different pcDNA3 expression plasmids, 1.0 μg each was used. Similar results were obtained in three separate experiments.