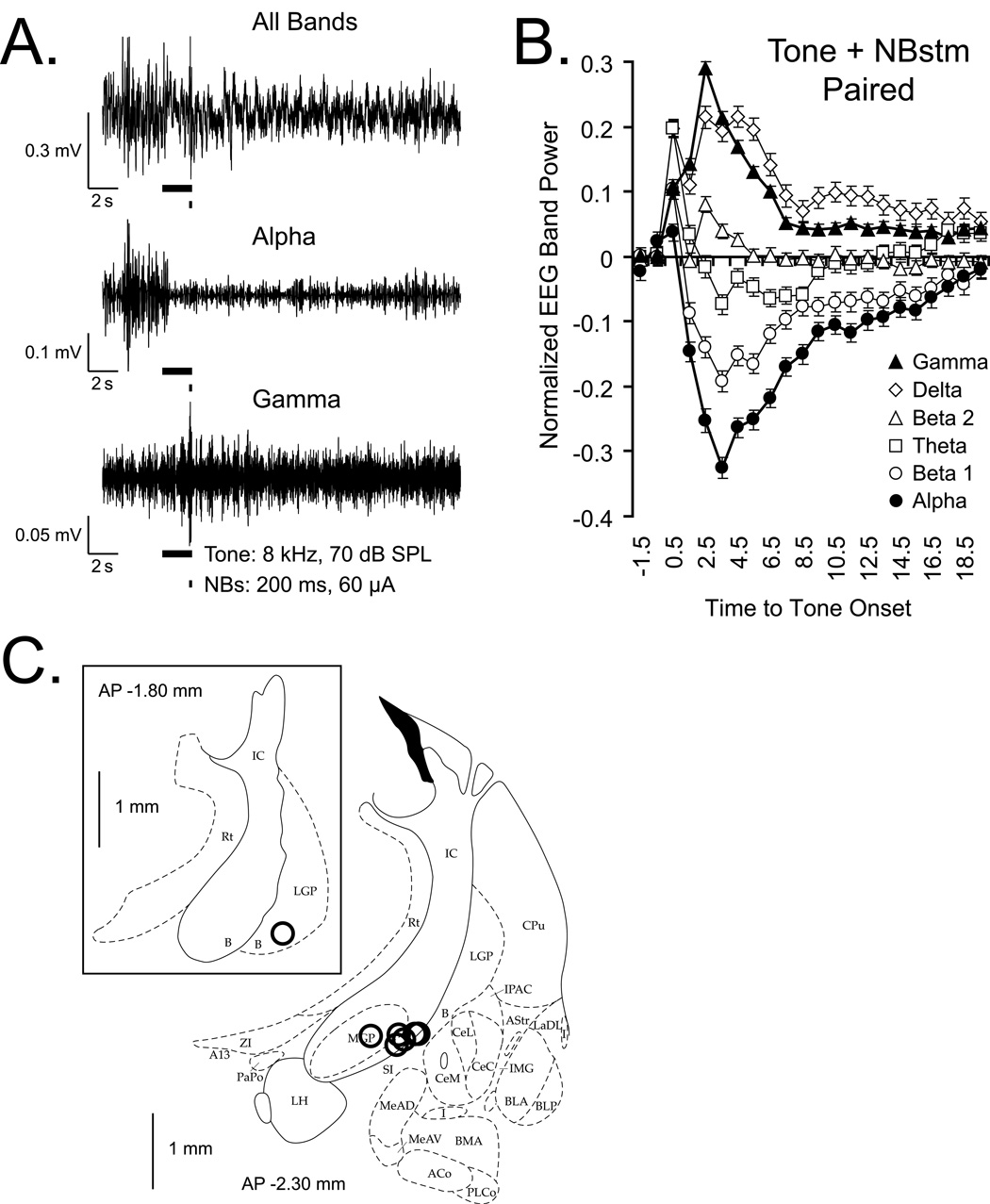
Figure 2.
Changes in the auditory cortical EEG during tone-NBstm pairing, and NB stimulation sites. (A) Example of changes in the EEG frequency bands that exhibited the largest changes in power. “All Bands”: original records obtained with band-pass filters set at 1–1000 Hz. “Alpha” and “Gamma”: corresponding records band-passed with digital filters set at 8.8–14.6 Hz to emphasize alpha and 33–59 Hz to emphasize gamma bands, respectively. This example is for a pairing trial (tone = 8.0 kHz, 70 db, 2s, with 200 ms overlapping train, 100 Hz, 60 µA bipolar stimulation of the NB) in unanesthetized rat. Black bars show tone and NBstim. Note the EEG activation, including a distinct decrease in higher voltage, slower waves (“Alpha”) and increase in lower voltage faster waves (“Gamma”). During pairing, EEG activation reflects a combination of effects of the NBstm and its preceding tone. (B) Group mean EEG spectral changes relative to pre-NBstm, computed as the EEG Power Change Index: EEG PCIi = (Posti − Pre) / (Posti + Pre) where the “Pre” period was the mean of the first 2 s out of four immediately preceding tone onset and post measures were calculated for consecutive periods of 1 s. Note major effects are an increase in gamma (closed triangles) and a decrease in alpha (closed circles) power. (C) Stimulating loci reconstructed for the NB-Mem animals. Sites of nucleus basalis stimulation projected onto outlines of frontal section at closest relevant sections anterior to posterior (AP) distance caudal from Bregma in millimeters (Paxinos & Watson, 1997). In all animals, stimulation was within the caudal nucleus basalis (ventrolateral internal capsule, ventromedial lateral globus pallidus and nucleus basalis of Meynart) which projects preferentially to the auditory cortex. The stimulation sites in 6 animals were found at AP −2.3, and in one animal — at AP −1.8 (insert). Abbreviations: B, basal nucleus of Meynert; CeM, amygdala central nucleus medial; CeL, amygdala central nucleus lateral; CPu, caudate–putamen; IC, internal capsule; IPAC, interstitial nucleus of posterior limb of anterior commissure; LGP, lateral globus pallidus; LH, lateral hypothalamus; SI, substantia innominata; SIB, substantia innominata, basal; SIV, substantia innominata, ventral.