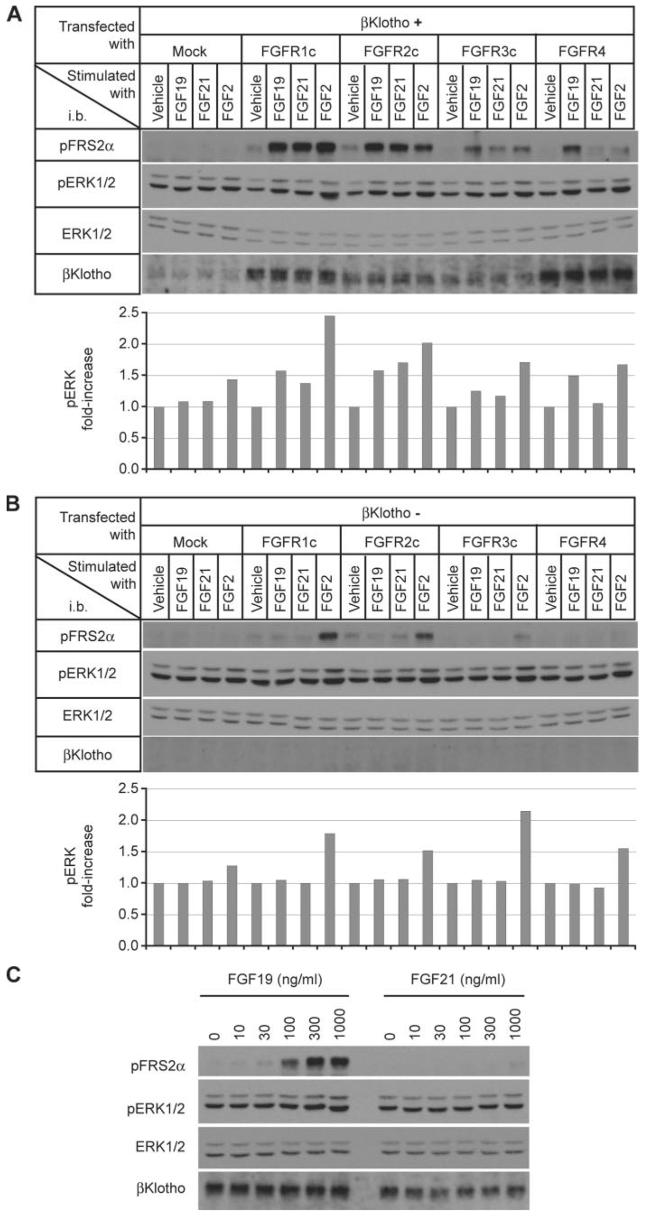
FIGURE 4. FGF19, but not FGF21, signals through the βKlotho-FGFR4 complex.
A, L6 cells were cotransfected with expression vectors for βKlotho and one of the indicated FGFR isoforms, then stimulated with FGF19 (1,000 ng/ml), FGF21 (1,000 ng/ml), or FGF2 (100 ng/ml) for 10 min. FGF signaling activity was determined by immunoblot (i.b.) analysis for phosphorylated FRS2α (pFRS2α) and phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pERK1/2) and total ERK1/2 (ERK1/2) levels performed as an internal control (upper panel). The signal intensity of phosphorylated ERK1/2 was quantified, corrected with that of corresponding total ERK1/2, and indicated as fold increase from vehicle-treated samples in each FGFR group (lower panel). A representative result from three independent experiments is shown. B, as in A, except that βKlotho was not transfected. C, dose response of FGF19 and FGF21 signaling in L6 cells cotransfected with expression vectors for βKlotho and FGFR4. The cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis as in A.