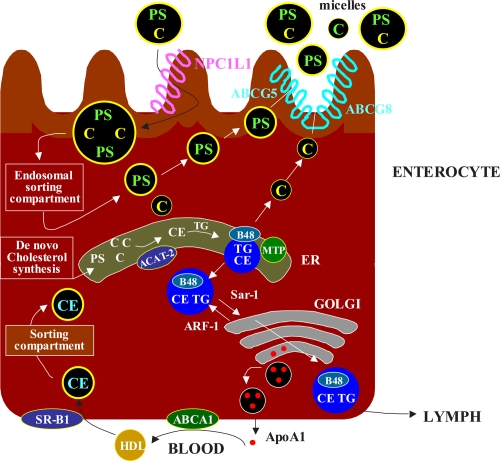
Figure 2.
Overview of the principal steps in the intestinal absorption of cholesterol(C). The intraluminal phase involves the digestion/hydrolysis of dietary lipids and micellar solubilization of cholesterol. The membrane transport phase involves cholesterol release from micelles at the brush border membrane and uptake into enterocytes via several sterol transporters, including Niemann-Pick C1like 1 protein(NPC1L1), aminopeptidase N(CD13), and annexin-2/caveolin-1(ANX2/CAV1). The brush border membrane also contains ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters(ABCG5 and ABCG8), which primarily move plant sterols and to a lesser extent cholesterol out of the enterocytes.