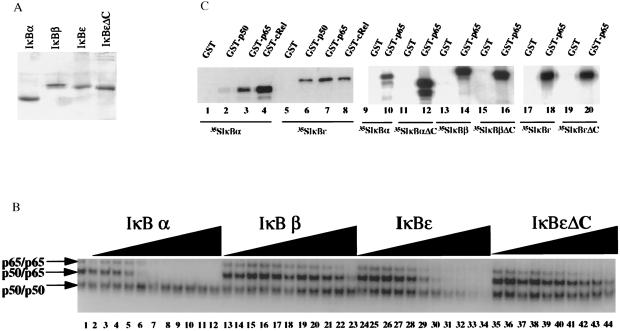
Figure 2.
IκBɛ removes NF-κB from the DNA in vitro. (A) Shown is a Coomassie blue-stained SDS/PAGE gel displaying the purified IκB proteins used in this study. (B) Shown is an EMSA experiment performed with an equimolar mixture of p50 and p65 homodimers and p50/p65 heterodimer in the presence or absence of increasing concentrations of recombinant IκBα, IκBβ, IκBɛ, and IκBɛΔC. The molar ratio between IκB proteins and NF-κB proteins was 1:16, 1:8, 1:4, 1:2, 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 6:1, 10:1, 16:1, and 24:1. (C) Protein–protein interactions between members of the Rel and IκB family of proteins. Lanes 1–8, in vitro translated and 35S-labeled IκBα (lanes 1–4) and IκBɛ (lanes 5–8) were incubated with glutatione beads harboring GST alone (lanes 1 and 5), GST-p50 (lanes 2 and 6), GST-p65 (lanes 3 and 7), or GST-cRel (lanes 4 and 8). Lanes 9–20, in vitro translated and 35S-labeled IκBα (lanes 9 and 10), IκBαΔC (lanes 11 and 12), IκBβ (lanes 13 and 14), IκBβΔC (lanes 15 and 16), IκBɛ (lanes 17 and 18), and IκBɛΔC (lanes 19 and 20) were incubated with glutathione beads harboring GST alone (lanes 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, and 19) or GST-p65 (lanes 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, and 20). The bound proteins were analyzed by PAGE and visualized by autoradiography.