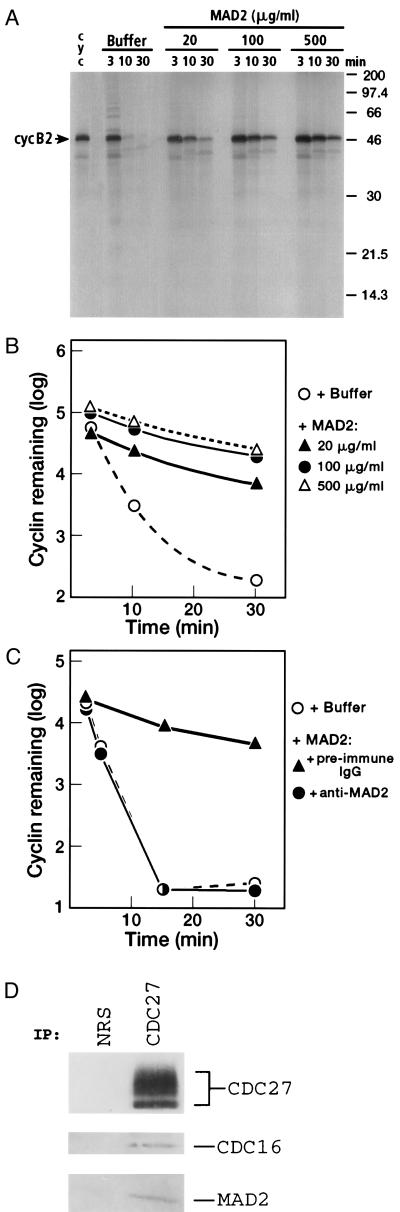
Figure 3.
Inhibition of [35S]cyclin B2 proteolysis in Δ90-arrested Xenopus egg extracts by human MAD2. (A) Dose-dependent inhibition of [35S]cyclin B2 degradation by MAD2 in Δ90-arrested extracts. Different concentrations of MAD2 were used in the assay as indicated, with buffer (10 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 7.4/10 mM NaCl) used as a control. (B) Cyclin B2 degradation in the presence of different concentrations of MAD2 was quantitated by PhosphorImager analysis. The amount of [35S]cyclin B2 remaining in the assay mixture vs. time is expressed as the logarithm of the relative density of the cyclin B band. (C) [35S]cyclin B2 degradation in the presence of anti-MAD2 antibodies. MAD2 (3.75 μg) was preincubated with 10 μg of either preimmune IgG or affinity-purified anti-MAD2 antibodies (22) for 40 min at 23°C, and then added to Δ90-arrested extracts. (Final concentration of MAD2 in the assay was 0.25 mg/ml). The amount of [35S]cyclin B2 remaining in the assay vs. time was determined as described in B. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation of exogenously added MAD2 with Xenopus egg cyclosome components. MAD2 (0.5 mg/ml) was added to Δ90-arrested extract and immunoprecipitated with anti-CDC27 antibodies or normal rabbit serum (NRS) as a control.