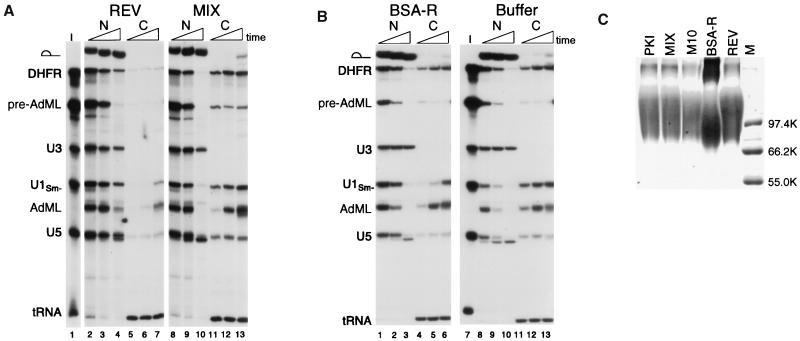
Figure 2.
Inhibition of mRNA export by the REV NES conjugate. (A) The REV NES conjugate inhibits mRNA and snRNA export when present in high amounts. Mixtures containing 32P-labeled DHFR mRNA, AdML pre-mRNA, U3 snRNA, U1Sm− snRNA, U5 snRNA, and tRNAiMet (I, lane 1) were coinjected into oocyte nuclei together with ≈130 ng per nucleus of the REV (lanes 2–7) or the MIX (lanes 8–13) peptide conjugates. Oocytes were dissected 1.5, 4, and 21 hr after injection, and RNA export was analyzed as in Fig. 1. The export of a small amount of pre-AdML RNA is because of saturation of the splicing machinery by the bolus of injected RNA. (B) The BSA-R conjugate fails to inhibit mRNA export even when present in high amounts. Mixtures containing 32P-labeled DHFR mRNA, AdML pre-mRNA, U3 snRNA, U1Sm− snRNA, U5 snRNA, and tRNAiMet (I, lane 7) were coinjected into oocyte nuclei together with ≈190 ng per nucleus of the BSA-R (lanes 1–6) conjugate or with buffer alone (lanes 8–13). Oocytes were dissected 1.5, 4, and 18.5 hr after injection, and RNA export was analyzed as in Fig. 1. (C) SDS/PAGE analysis of peptide conjugates. Ten micrograms of each of the indicated peptide conjugates (Table 1) were subjected to electrophoresis in an SDS-containing 8% polyacrylamide gel, and the proteins were detected by Coomassie blue staining. The marker (M) lane contains 0.5 μg of each protein molecular weight marker (Promega).