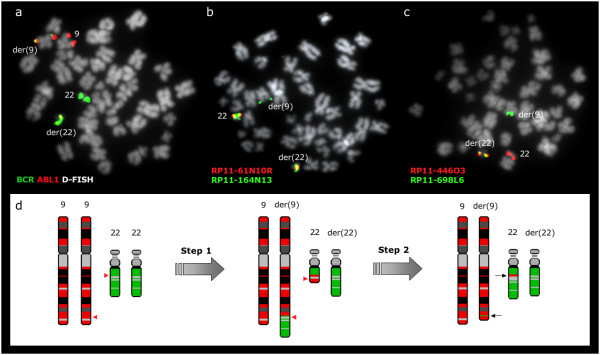
Figure 4.
BCR/ABL1 at 22q11.2 in patient no 4 results from a multiple step mechanism. (a) BCR/ABL1 D-FISH probe (Vysis) showing 1 red, 1 green, and 2 fusion signals. The presence of both BCR/ABL1 and ABL1/BCR fusion genes is an evidence of an initial t(9;22)(q34;q11.2). (b) A representative metaphase cell with co-hybridization of FISH probes RP11-61N10 and RP11-164N13, showing a split signal from RP11-164N13. Thus, the proximal boundary of the 22q11.2 sequences identified within the structure of the der(9) chromosome coincides with the BCR breakpoint. (c) A representative metaphase cell with co-hybridization of FISH probes RP11-698L6 and RP11-446O3. RP11-698L6 is identified at der(9) while RP11-446O3 is found at der(22). The distal breakpoint of the 22q11.2 fragment lies between these two BAC clones. (d) Schematic representation of the multiple step rearrangement with chromosomes 9 in red and 22 in green. Red arrowheads show the breakpoints. The presence of both 9q34 sequences inserted on der(22) and 22q11.2 sequences inserted on der(9) (black arrows) can be explained by two consecutive translocations: an initial t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) followed by a second reciprocal translocation between the two products, with breakpoints distal to both BCR/ABL1 and ABL1/BCR fusion genes.