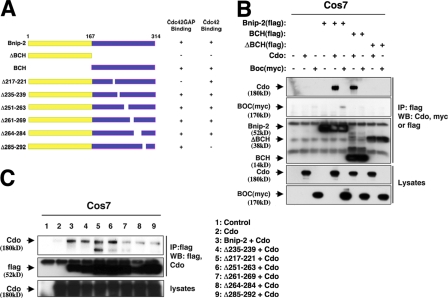
Figure 2.
Cdo binds the BCH domain of Bnip-2. (A) Schematic of Bnip-2 and Bnip-2 deletion mutants and their ability to bind Cdc42GAP and Cdc42 (summarized from Low et al., 2000b; Zhou et al., 2005). Note that Δ217–221 and Δ235–239 are also known as ΔM and ΔR, respectively (Low et al., 2000b; Zhou et al., 2005). (B) Lysates of COS7 cells transiently transfected with flag-tagged Bnip-2, flag-tagged BCH, flag-tagged ΔBCH, Cdo, myc-tagged Boc, or control (−) expression vectors as indicated were immunoprecipitated (IP) with flag epitope antibodies and then Western blotted with flag epitope, Cdo, or myc epitope antibodies. (C) Lysates of COS7 cells transiently transfected with flag-tagged Bnip-2, flag-tagged Bnip-2 deletion mutants, Cdo, or control (−) expression vectors as indicated were immunoprecipitated (IP) with flag epitope antibodies and then Western blotted with flag epitope or Cdo antibodies. For unknown reasons, a faster migrating Cdo degradation band is reproducibly seen when Cdo is coexpressed with the Δ217–221 mutant. Lower levels of this band are also seen when Cdo is coexpressed with the Δ251–263 and Δ261–269 mutants.