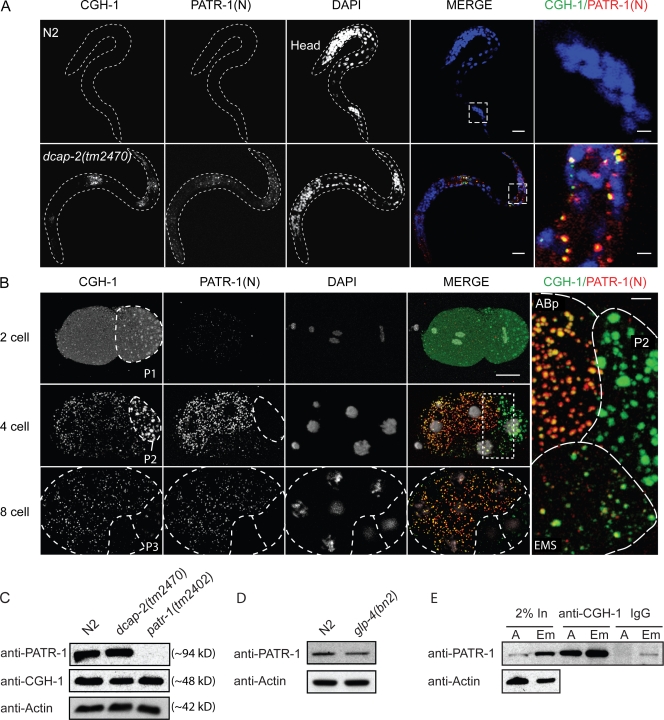
Figure 3.
Association of CGH-1 and PATR-1 in somatic P bodies. (A) Somatic P bodies in dcap-2(tm2470) larvae. Single-plane confocal images reveal colocalizing CGH-1 (green) and PATR-1(N)-staining (red) particles in many somatic cells in dcap-2(tm2470) but not N2 (WT) L1-stage larvae (outlined by broken lines). Regions outlined by dashed boxes are enlarged on the far right. n > 100 for each set. Bars: 10 μm; (far right) 2 μm. (B) PATR-1(N) staining marks somatic P bodies in the embryo. WT embryos were analyzed by antibody staining and confocal microscopy (z series projections are shown). Germ cell precursors are outlined by broken lines, and in eight-cell embryos, the somatic sister of P3 (C blastomere) is similarly delineated. Robust PATR-1(N) staining is first detected in four-cell embryos, in which it colocalizes with CGH-1 in somatic blastomeres. After each successive division of the germ cell precursor PATR-1(N), staining is initially low, then increases. These low levels are apparent in the EMS blastomere (detail of the boxed area shown on the right), and also in the C blastomere (sister of P3) at the eight-cell stage. More than 50 embryos in each set were examined in each of at least two experiments. Bars: 10 μm; (far right) 2 μm. (C) CGH-1 and PATR-1 levels in N2, dcap-2(tm2470), and patr-1(2402) adult hermaphrodites. PATR-1 was detected with anti–PATR-1(N). (D) PATR-1 expression in N2 and glp-4(bn2) adults, which essentially lack germ cells when grown at the restrictive temperature of 25°C. Densitometry indicated that glp-4(bn2) adult PATR-1 levels were ∼68% of WT. (E) PATR-1 coIPs with CGH-1. CGH-1 IPs from 2.5 mg of adult (A) and embryo (Em) protein extracts were Western blotted for PATR-1.