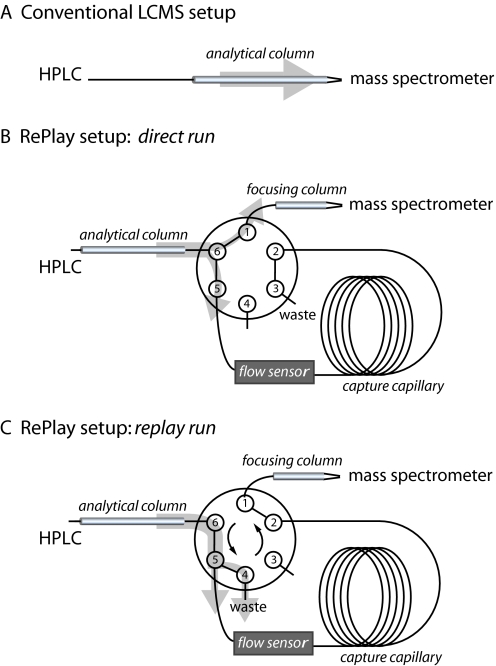
Fig. 1.
Schematics of the conventional LCMS and the RePlay setup. A, conventional LCMS setup using a column with an integrated emitter placed in front of the mass spectrometer. The light gray arrow indicates the direction of the flow. B, in the “direct run” of the RePlay setup the six-port splitting valve is positioned such that part of the effluent of the first nano-LC column (“analytical column”) flows to the mass spectrometer via a short second column (“focusing column”). The other part is stored in a long capture capillary, which has the volume appropriate to hold the complete gradient. C, when the valve is switched the stored gradient is directed to the mass spectrometer (“replay run”). Capture capillaries of different lengths serve as split adjusters, at port 3 in the direct run and port 4 in the RePlay run, and control the split ratio, which is read out by the flow sensor. The split adjuster at port 4 can be replaced by a plug, but a split allows higher flow rates and reduces the time used for washing and loading of the analytical column.