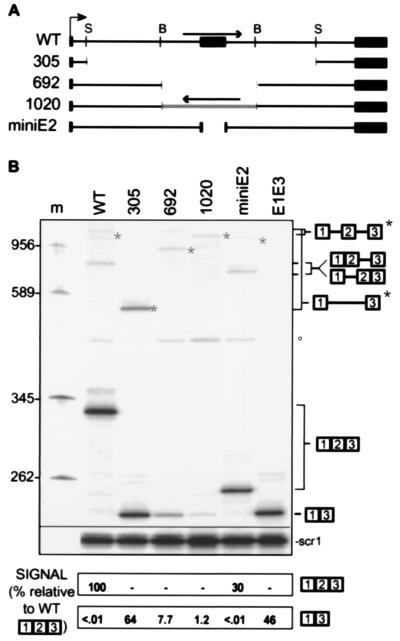
Figure 2.
Compatibility of YL8A splice sites and influence of internal exon sequences on exon inclusion. (A) Structure of mutant substrates. Single intron substrates with chimeric introns of 305 and 692 nucleotides (deleted regions are depicted as gaps) and 1,020 nucleotides (the inverted region spans exon 2) are shown. The two-intron miniE2 substrate lacks 72 of 94 nucleotides from the internal exon. (B) Splicing phenotypes of the mutant constructs. Splicing was analyzed by reverse transcription of total cell RNA using a 5′-labeled (32P) primer complementary to CUP1 sequences. Lane m, DNA size markers. E1E3 is a marker for exon skipping expressed from a construct in which exons 1 and 3 are directly fused. Expected products are diagrammed at the right. The different unspliced pre-mRNAs are indicated by an asterisk (∗). Spliced products were measured relative to scr1; the amount of exon included mRNA in wild type was taken as 100%.