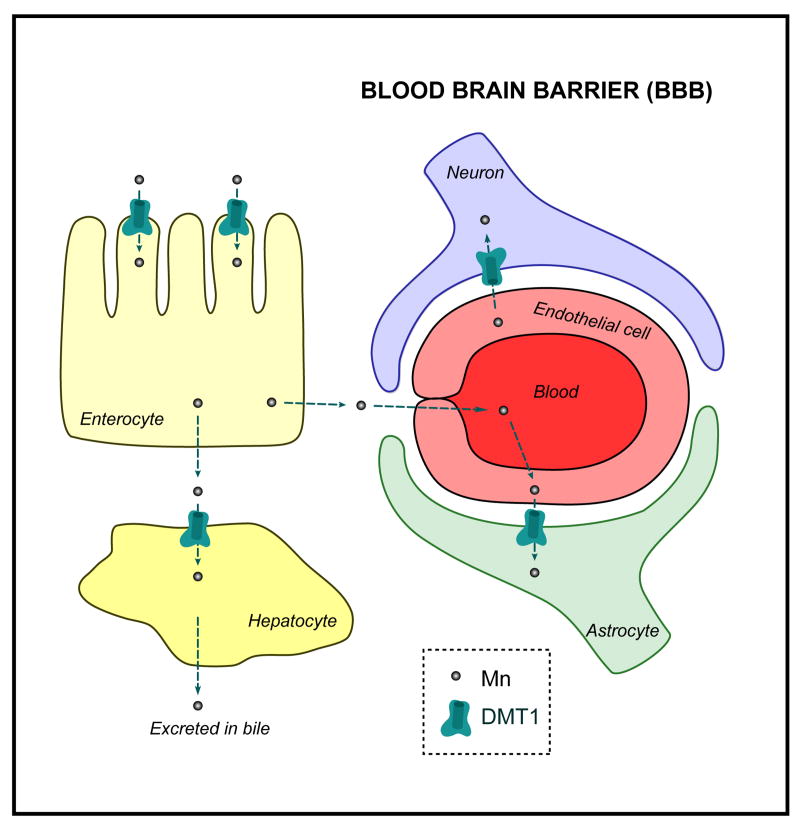
Figure 3. Mn uptake via DMT1 in vertebrates.
DMT1 is present at the plasma membrane where it is responsible for Mn cellular uptake. Mn is primarily taken up by entorocytes via DMT1 before reaching the adjacent tissues and the blood. Part of it is then excreted in the bile after absorption by the liver, while some accumulates in the brain after crossing the BBB via DMT1 expressed in glial cells and neurons. Mn uptake mechanisms independent of DMT1 are not represented here.