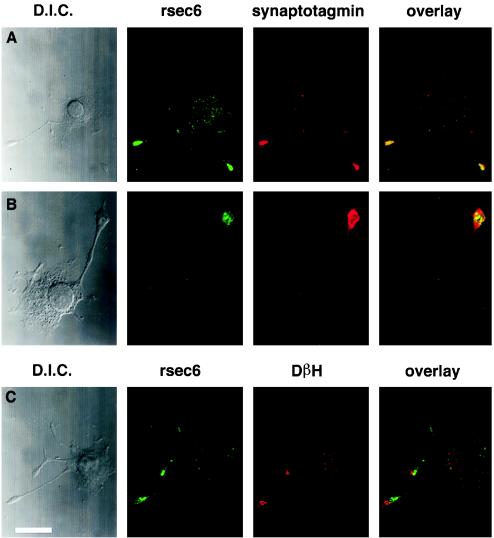
Figure 5.
rsec6 colocalizes with vesicles and sites of exocytosis in nerve growth factor-differentiated PC12 cells. (A and B) Comparison of the distribution of rsec6 and the synaptic vesicle marker, synaptotagmin, in PC12 cells that have been differentiated with nerve growth factor for 2 days demonstrated by double immunofluorescence. The antibodies used are listed above their respective fluorescence micrographs. Differential interference contrast micrographs of each cell are shown on the left. A shows that rsec6 immunofluorescence is more intense in the vesicle-rich terminals of growing neurites with lighter labeling in the cell body. (B) A higher magnification view reveals the punctate distribution of rsec6 in the neurite terminal. (C) rsec6 is also found at sites of Ca2+-regulated secretion as demonstrated by the presence of DβH on the cell surface. Antibodies directed against DβH were applied in the absence of detergent to reveal cell-surface sites of recent exocytosis in response to K+/Ca2+-induced depolarization. Subsequent application of antibodies to rsec6 in the presence of detergent reveal the distribution of internal rsec6. The overlay micrograph demonstrates the contrast between intracellular rsec6 localization and cell-surface DβH distribution. Bar (in C) = 7.8 μm (A), 3.3 μm (B), 6.8 μm (C).