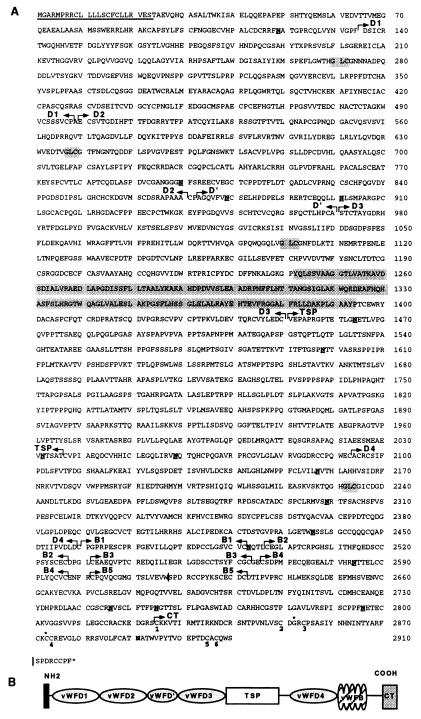
Figure 2.
(A) Deduced amino acid sequence of otogelin. The signal peptide is underlined. Arrows delineate the different protein domains. WF D-type domains D1 (residues 135–498), D2 (500–870), D′ (873–971, truncated domain), D3 (972–1450), and D4 (2093–2459) share between each other and with the D domains of WF a sequence similarity of about 50%. The D3 domain contains a unique 103-residue insertion (position 1242–1394), which is shaded. The conserved residues of the multimerization site are shaded. Five WF B-type domains, B1 (2460–2492), B2 (2497–2527), B3 (2532–2563), B4 (2266–2597), B5 (2602–2632) are shown. The TSP domain (1451–2036) contains 13% threonines, 13% serines, and 15% prolines and is devoid of cysteine; CT, carboxyl-terminal end (2825–2910). The potential N-glycosylation sites are underlined and in bold. | indicates the additional 3′ RACE PCR alternatively spliced sequence presented at the end of the sequence. The cysteine involved in the dimerization of WF and TGF-β2 (position 2873) and the conserved glycine (position 2852) are indicated by an asterisk. The cysteines involved in the TGF-β2 knot cystine structure formation are numbered. (B) Schematic representation of the structure of otogelin. The thick bar indicates the predicted signal peptide.