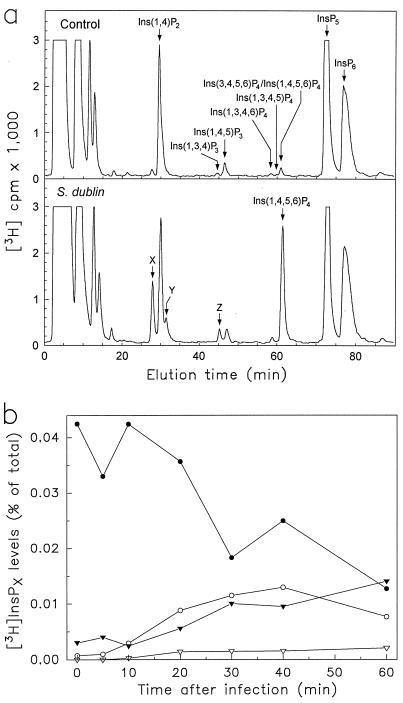
Figure 1.
HPLC analysis of inositol polyphosphate levels after S. dublin infection of T84 human colonic epithelial cells. [3H]Inositol-labeled T84 monolayers were infected with S. dublin, and inositol polyphosphates were extracted and analyzed by an HPLC system that resolves three InsP4 peaks, as demonstrated (17). (a) A representative radiochromatogram from control cells (top) and cells infected for 30 min with S. dublin (bottom). Arrows indicate elution times of known inositol phosphate standards. The Ins(3,4,5,6)P4/Ins(1,4,5,6)P4 peak was collected and analyzed as described in Materials and Methods and found to consist of 84 ± 5% (mean ± SEM, n = 3) Ins(1,4,5,6)P4 after S. dublin infection, with the remainder being Ins(3,4,5,6)P4. In unstimulated cells, the same peak contained approximately equal amounts of both isomers (data not shown) (6). (b) A time course of the levels of InsP5 (•), Ins(1,4,5,6)P4 (○), InsP3-Z (▿), and InsP2-X and Y (▾). Data are displayed as the fraction of radioactivity associated with the specific InsPx relative to the total radioactivity in all cellular InsPx.